 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Cuprimine, Cuprenyl, Depen, others |
| Other names |
|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a618021 |
| License data | |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | By mouth (capsules) |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | Variable |
| Metabolism | Liver |
| Elimination half-life | 1 hour |
| Excretion | Kidney |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.136 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
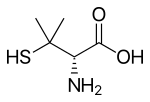
| Formula | C5H11NO2S |
| Molar mass | 149.21 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Penicillamine, sold under the brand name of Cuprimine among others, is a medication primarily used for the treatment of Wilson's disease.[1] It is also used for people with kidney stones who have high urine cystine levels, rheumatoid arthritis, and various heavy metal poisonings.[1][2] It is taken by mouth.[2]
Penicillamine was approved for medical use in the United States in 1970.[1] It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines.[3]
- ^ a b c "Penicillamine". The American Society of Health-System Pharmacists. Archived from the original on 21 December 2016. Retrieved 8 December 2016.
- ^ a b Cite error: The named reference
WHO2008was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ World Health Organization (2019). World Health Organization model list of essential medicines: 21st list 2019. Geneva. hdl:10665/325771. WHO/MVP/EMP/IAU/2019.06. License: CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 IGO.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link)