
| |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Systematic IUPAC name
Permanganate | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| MnO− 4 | |
| Molar mass | 118.934 g·mol−1 |
| Conjugate acid | Permanganic acid |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
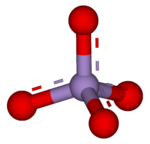
A permanganate (/pərˈmæŋɡəneɪt, pɜːr-/)[1] is a chemical compound with the manganate(VII) ion, MnO−
4, the conjugate base of permanganic acid. Because the manganese atom has a +7 oxidation state, the permanganate(VII) ion is a strong oxidising agent. The ion is a transition metal ion with a tetrahedral structure.[2] Permanganate solutions are purple in colour and are stable in neutral or slightly alkaline media. The exact chemical reaction depends on the carbon-containing reactants present and the oxidant used. For example, trichloroethane (C2H3Cl3) is oxidised by permanganate ions to form carbon dioxide (CO2), manganese dioxide (MnO2), hydrogen ions (H+), and chloride ions (Cl−).[3]
- 8MnO−
4 + 3C
2H
3Cl
3 → 6CO
2 + 8MnO
2 + H+
+ 4H
2O + 9Cl−
In an acidic solution, permanganate(VII) is reduced to the pale pink manganese(II) (Mn2+) with an oxidation state of +2.
- 8 H+
+ MnO−
4 + 5 e− → Mn2+ + 4 H2O
In a strongly basic or alkaline solution, permanganate(VII) is reduced to the green manganate ion, MnO2−
4 with an oxidation state of +6.
- MnO−
4 + e− → MnO2−
4
In a neutral solution, however, it gets reduced to the brown manganese dioxide MnO2 with an oxidation state of +4.
- 2 H2O + MnO−
4 + 3 e− → MnO2 + 4 OH−
- ^ "permanganate". Merriam-Webster.com Dictionary. Merriam-Webster.
- ^ Sukalyan Dash, Sabita Patel & Bijay K. Mishra (2009). "Oxidation by permanganate: synthetic and mechanistic aspects". Tetrahedron. 65 (4): 707–739. doi:10.1016/j.tet.2008.10.038.
- ^ "Geo-Cleanse International, INC. | Permanganate".