| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
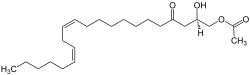
| Preferred IUPAC name
(2R,12Z,15Z)-2-Hydroxy-4-oxohenicosa-12,15-dien-1-yl acetate | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| Properties | |
| C23H40O4 | |
| Molar mass | 380.569 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Persin is a fungicidal toxin present in the avocado.[1] Persin is an oil-soluble compound structurally similar to a fatty acid, a colourless oil, and it leaches into the body of the fruit from the seeds.
The relatively low concentrations of persin in the ripe pulp of the avocado fruit is generally considered harmless to humans. Negative effects in humans are primarily in allergic individuals. When persin is consumed by domestic animals through the leaves or bark of the avocado tree, or skins and seeds of the avocado fruit, it is toxic and dangerous.[2][3]
- ^ Oelrichs PB, Ng JC, Seawright AA, Ward A, Schäffeler L, MacLeod JK (1995). "Isolation and identification of a compound from avocado (Persea americana) leaves which causes necrosis of the acinar epithelium of the lactating mammary gland and the myocardium". Nat. Toxins. 3 (5): 344–9. doi:10.1002/nt.2620030504. PMID 8581318.
non-fatal injury to the lactating mammary gland of the mouse is from 60 to 100 mg/kg. At doses of person above 100 mg/kg, necrosis of myocardial fibres may occur and areas of myocardial fibrosis can be observed in animals surviving for seven days. Hydrothorax and/or pulmonary oedema may be present in more severely affected animals. [..] there have been few attempts to investigate the cause of possible toxic effects of the plant in mammals.
- ^ ASPCA Poison Control: Avocado on aspca.org
- ^ Morton, Julia F. "NewCROP - Avocado Persea americana". hort.purdue.edu. Purdue University. Retrieved 3 December 2017.