Parts of this article (those related to 2012–present) need to be updated. (April 2016) |

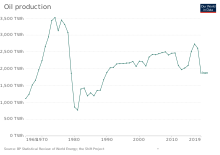
Iran is an energy superpower and the petroleum industry in Iran plays an important part in it.[2][3][4] In 2004, Iran produced 5.1 percent of the world's total crude oil (3.9 million barrels (620,000 m3; 160 million US gal) per day), which generated revenues of US$25 billion to US$30 billion and was the country's primary source of foreign currency.[5][6] At 2006 levels of production, oil proceeds represented about 18.7% of gross domestic product (GDP). However, the importance of the hydrocarbon sector to Iran's economy has been far greater. The oil and gas industry has been the engine of economic growth, directly affecting public development projects, the government's annual budget, and most foreign exchange sources.[5]
In FY 2009, the sector accounted for 60% of total government revenues and 80% of the total annual value of both exports and foreign currency earnings.[citation needed] Oil and gas revenues are affected by the value of crude oil on the international market. It has been estimated that at the Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC) quota level (December 2004), a one-dollar change in the price of crude oil on the international market would alter Iran's oil revenues by US$1 billion.[5]
In 2012, Iran, which exported around 1.5 million barrels of crude oil a day, was the second-largest exporter among the Organization of Petroleum Exporting Countries.[7] In the same year, officials in Iran estimated that Iran's annual oil and gas revenues could reach $250 billion by 2015.[8] However, the industry was disrupted by an international embargo from July 2012 to January 2016.[9][10] Iran plans to invest a total of $500 billion in the oil sector before 2025.[11][12]
- ^ SHANA: Share of domestically made equipments on the rise Archived 2012-03-09 at the Wayback Machine. Retrieved July 26, 2010.
- ^ Energy and the Iranian economy. DIANE. July 25, 2006. ISBN 9781422320945. Archived from the original on April 7, 2016. Retrieved April 14, 2016.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|agency=ignored (help) - ^ Bezen, Balamir Coşkun (2009). "Global Energy Geopolitics and Iran" (PDF). Uluslararası İlişkiler. 5 (20): 179–201. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2014-04-01. Retrieved 2016-10-29.
- ^ "The Rising might of the Middle East super power - Council on Foreign Relations". Cfr.org. Archived from the original on 2016-03-03. Retrieved 2012-02-07.
- ^ a b c Kurtis, Glenn; Eric Hooglund. Iran, a country study. Washington D.C.: Library of Congress. pp. 160–163. ISBN 978-0-8444-1187-3. Retrieved November 21, 2010.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- ^ "Iran's Foreign Trade Regime Report" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2013-03-10. Retrieved 2010-08-11.
- ^ "Sanctions reduced Iran's oil exports and revenues in 2012". EIA. Apr 26, 2013. Archived from the original on February 1, 2014. Retrieved May 13, 2013.
- ^ Mehr News Agency: Iran eyes $250 billion annual revenue in 5 years Archived 2018-07-17 at the Wayback Machine Retrieved December 22, 2010
- ^ Nasseri, Ladane (12 February 2012). "Iran Won't Yield to Pressure, Foreign Minister Says; Nuclear News Awaited". Bloomberg News. Archived from the original on 23 December 2014. Retrieved 14 April 2016.
- ^ Chuck, Elizabeth (16 January 2016). "Iran Sanctions Lifted After Watchdog Verifies Nuclear Compliance". Reuters. Archived from the original on 23 March 2016. Retrieved 14 April 2016.
- ^ Iran Daily - Domestic Economy - 04/24/08 [dead link]
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
heritagewas invoked but never defined (see the help page).