 | |
| Woodwind instrument | |
|---|---|
| Classification | |
| Hornbostel–Sachs classification | 421.121.12-71 (Flute-like aerophone with keys) |
| Playing range | |
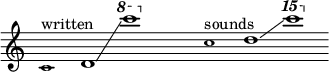 | |
| Related instruments | |
| Flutes: | |
The piccolo (/ˈpɪkəloʊ/ PIH-kə-loh; Italian for 'small')[1][2] is a half-size flute and a member of the woodwind family of musical instruments. Sometimes referred to as a "baby flute" or piccolo flute, the modern piccolo has the same type of fingerings as the standard transverse flute,[3] but the sound it produces is an octave higher. This has given rise to the name ottavino[a] (Italian pronunciation: [ottaˈviːno]), by which the instrument is called in Italian[4] and thus also in scores of Italian composers.

Piccolos are often orchestrated to double the violins or the flutes, adding sparkle and brilliance to the overall sound because of the aforementioned one-octave transposition upwards. The piccolo is a standard member in orchestras, marching bands, and wind ensembles.
- ^ "Piccolo". Merriam-Webster. Retrieved 2012-05-26.
- ^ "piccolo - Dictionary Definition". Vocabulary.com. Retrieved 2021-01-25.
- ^ "Transverse flute". The Free Dictionary By Farlex. Retrieved 2012-05-26.
- ^ "The Names of Instruments and Voices in English, French, German, Italian, Russian, and Spanish". Yale University Music Library. Retrieved 2012-05-26.
Cite error: There are <ref group=lower-alpha> tags or {{efn}} templates on this page, but the references will not show without a {{reflist|group=lower-alpha}} template or {{notelist}} template (see the help page).