| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
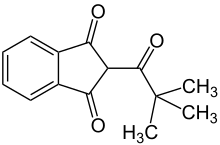
| Preferred IUPAC name
2-(2,2-Dimethylpropanoyl)-1H-indene-1,3(2H)-dione | |
| Other names
2-Pivaloyl-1,3-indandione
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.001.330 |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C14H14O3 | |
| Molar mass | 230.26 g/mol |
| Appearance | Bright-yellow powder[1] |
| Odor | almost none |
| Density | 1.06 g/mL |
| Melting point | 110 °C (230 °F; 383 K) |
| 0.002% (25°C)[1] | |
| Hazards | |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
LD50 (median dose)
|
280 mg/kg (rat, oral) 75 mg/kg (dog, oral) 150 mg/kg (rabbit, oral)[2] |
| NIOSH (US health exposure limits): | |
PEL (Permissible)
|
TWA 0.1 mg/m3[1] |
REL (Recommended)
|
TWA 0.1 mg/m3[1] |
IDLH (Immediate danger)
|
100 mg/m3[1] |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Pindone is an anticoagulant drug[3] for agricultural use. It is commonly used as a rodenticide in the management of rat and rabbit populations.
It is pharmacologically analogous to warfarin and inhibits the synthesis of Vitamin K-dependent clotting factors.
- ^ a b c d e NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards. "#0516". National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- ^ "Pindone". Immediately Dangerous to Life or Health Concentrations (IDLH). National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- ^ Robinson MH, Twigg LE, Wheeler SH, Martin GR (March 2005). "Effect of the anticoagulant, pindone, on the breeding performance and survival of merino sheep, Ovis aries". Comp. Biochem. Physiol. B. 140 (3): 465–73. doi:10.1016/j.cbpc.2004.11.011. PMID 15694595.