
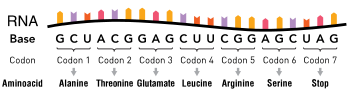
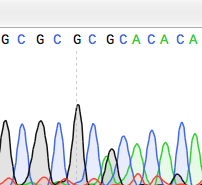
A point mutation is a genetic mutation where a single nucleotide base is changed, inserted or deleted from a DNA or RNA sequence of an organism's genome.[1] Point mutations have a variety of effects on the downstream protein product—consequences that are moderately predictable based upon the specifics of the mutation. These consequences can range from no effect (e.g. synonymous mutations) to deleterious effects (e.g. frameshift mutations), with regard to protein production, composition, and function.
- ^ "Point Mutation". Biology Dictionary. 22 November 2016. Retrieved 17 May 2019.