| Porcupine ray | |
|---|---|

| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Chondrichthyes |
| Subclass: | Elasmobranchii |
| Order: | Myliobatiformes |
| Family: | Dasyatidae |
| Genus: | Urogymnus |
| Species: | U. asperrimus
|
| Binomial name | |
| Urogymnus asperrimus (Bloch & J. G. Schneider, 1801)
| |
| |
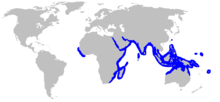
| Range of the porcupine ray[2] | |
| Synonyms | |
| |
The porcupine ray (Urogymnus asperrimus) is a rare species of stingray in the family Dasyatidae. This bottom-dweller is found throughout the tropical Indo-Pacific, as well as off West Africa. It favors sand, coral rubble, and seagrass habitats in inshore waters to a depth of 30 m (100 ft). A large and heavy-bodied species reaching 1.2–1.5 m (3.9–4.9 ft) in width, the porcupine ray has a nearly circular, plain-colored pectoral fin disc and a thin tail without any fin folds. Uniquely within its family, it lacks a venomous stinging spine. However, an adult ray can still defend itself ably with the many large, sharp thorns found over its disc and tail.
The diet of the porcupine ray consists mainly of benthic invertebrates and bony fishes, which it digs up from the sea floor. It is aplacental viviparous, in which the developing embryos are nourished by histotroph ("uterine milk") produced by the mother. The porcupine ray has long been valued for its rough and durable skin, which was made into a shagreen leather once used for various utilitarian and ornamental purposes, such as to cover sword hilts and shields. It is caught incidentally by coastal fisheries. Because it must be handled carefully due to its thorns, its commercial significance is limited. Unregulated fishing has led to this species declining in many parts of its range, thus it has been listed as Vulnerable by the International Union for Conservation of Nature.
- ^ Sherman, C.S.; Bennett, R.; Haque, A.B.; Jabado, R.W.; Rohner, C.A.; Simpfendorfer, C.; Van Beuningen, D. (2024). "Urogymnus asperrimus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2024: e.T39413A124411670. Retrieved 26 October 2024.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
last and stevenswas invoked but never defined (see the help page).
