The Viruses Portal
Welcome!
Viruses are small infectious agents that can replicate only inside the living cells of an organism. Viruses infect all forms of life, including animals, plants, fungi, bacteria and archaea. They are found in almost every ecosystem on Earth and are the most abundant type of biological entity, with millions of different types, although only about 6,000 viruses have been described in detail. Some viruses cause disease in humans, and others are responsible for economically important diseases of livestock and crops.
Virus particles (known as virions) consist of genetic material, which can be either DNA or RNA, wrapped in a protein coat called the capsid; some viruses also have an outer lipid envelope. The capsid can take simple helical or icosahedral forms, or more complex structures. The average virus is about 1/100 the size of the average bacterium, and most are too small to be seen directly with an optical microscope.
The origins of viruses are unclear: some may have evolved from plasmids, others from bacteria. Viruses are sometimes considered to be a life form, because they carry genetic material, reproduce and evolve through natural selection. However they lack key characteristics (such as cell structure) that are generally considered necessary to count as life. Because they possess some but not all such qualities, viruses have been described as "organisms at the edge of life".
Selected disease
Gastroenteritis is an inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract involving both the stomach and small intestine, which results in diarrhoea and vomiting, and sometimes abdominal pain. It is usually caused by a virus: most commonly rotavirus and norovirus, but also adenovirus and astrovirus. Other major infectious causes include Campylobacter, Escherichia coli, Vibrio cholerae and some other bacteria, as well as protozoa. Viruses, particularly rotavirus, cause about 70% of gastroenteritis episodes in children, while norovirus is the leading cause of gastroenteritis among adults in America, causing over 90% of outbreaks.
Transmission can be from consumption of improperly prepared foods or contaminated water, or by close contact with infectious individuals. Good sanitation practices and a convenient supply of uncontaminated water are important for reducing infection. Personal measures such as hand washing with soap can decrease incidence by as much as 30%. An estimated 2 billion cases of gastroenteritis occurred globally in 2015, mainly among children and people in developing countries, resulting in 1.3 million deaths. Gastroenteritis is usually an acute and self-limiting disease that does not require medication; the main treatment is rehydration using oral rehydration therapy. A rotavirus vaccine is available.
Selected image
Muhammad ibn Zakariya al-Razi was a Persian physician and chemist who, in the 9th century, was the first to document the distinction between the diseases of measles and smallpox.
Credit: Gerard of Cremona (c. 1250–60)
In the news
26 February: In the ongoing pandemic of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), more than 110 million confirmed cases, including 2.5 million deaths, have been documented globally since the outbreak began in December 2019. WHO
18 February: Seven asymptomatic cases of avian influenza A subtype H5N8, the first documented H5N8 cases in humans, are reported in Astrakhan Oblast, Russia, after more than 100,0000 hens died on a poultry farm in December. WHO
14 February: Seven cases of Ebola virus disease are reported in Gouécké, south-east Guinea. WHO
7 February: A case of Ebola virus disease is detected in North Kivu Province of the Democratic Republic of the Congo. WHO
4 February: An outbreak of Rift Valley fever is ongoing in Kenya, with 32 human cases, including 11 deaths, since the outbreak started in November. WHO
21 November: The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) gives emergency-use authorisation to casirivimab/imdevimab, a combination monoclonal antibody (mAb) therapy for non-hospitalised people twelve years and over with mild-to-moderate COVID-19, after granting emergency-use authorisation to the single mAb bamlanivimab earlier in the month. FDA 1, 2
18 November: The outbreak of Ebola virus disease in Équateur Province, Democratic Republic of the Congo, which started in June, has been declared over; a total of 130 cases were recorded, with 55 deaths. UN
Selected article
Virus classification is the process of naming viruses and placing them into a taxonomic system. They are mainly classified by phenotypic characteristics, such as morphology, nucleic acid type, mode of replication, host organisms and the type of disease they cause.
Two schemes are in common use. The International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses (ICTV), established in the early 1970s, classifies viruses into taxa (groups) similar to the biological classification used for cellular organisms, which reflect viruses believed to have a common ancestor. As of 2019, 9 kingdoms, 16 phyla, 36 classes, 55 orders, 168 families, 1,421 genera and 6,589 species of viruses have been defined. Since 2018, viruses have also been classified into higher-level taxa called realms. Four realms are defined, as of 2020, encompassing almost all RNA viruses; some DNA viruses have yet to be assigned a realm.
The older Baltimore classification (pictured), proposed in 1971 by David Baltimore, places viruses into seven groups (I–VII) based on their nucleic acid type, number of strands and sense, as well as the method the virus uses to generate mRNA. There is some concordance between Baltimore groups and the higher levels of the ICTV scheme.
Selected outbreak
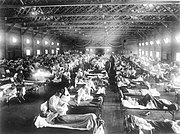
The 1918–20 influenza pandemic, the first of the two involving H1N1 influenza virus, was unusually deadly. It infected 500 million people across the entire globe, with a death toll of 50–100 million (3–5% of the world's population), making it one of the deadliest natural disasters of human history. It has also been implicated in the outbreak of encephalitis lethargica in the 1920s. Despite the nickname "Spanish flu", the pandemic's geographic origin is unknown.
Most influenza outbreaks disproportionately kill young, elderly or already weakened patients; in contrast this predominantly killed healthy young adults. Contemporary medical reports suggest that malnourishment, overcrowded medical facilities and poor hygiene promoted fatal bacterial pneumonia. Some research suggests that the virus might have killed through a cytokine storm, an overreaction of the body's immune system. This would mean the strong immune reactions of young adults resulted in a more severe disease than the weaker immune systems of children and older adults.
Selected quotation
| “ | We are part virus. This bizarre yet inescapable fact has been revealed over the past 30 years, as scientists have spelunked their way through the human genome and encountered stretches of DNA with the telltale chemical signatures of viruses. | ” |
Recommended articles
Viruses & Subviral agents: bat virome • elephant endotheliotropic herpesvirus • HIV • introduction to viruses![]() • Playa de Oro virus • poliovirus • prion • rotavirus
• Playa de Oro virus • poliovirus • prion • rotavirus![]() • virus
• virus![]()
Diseases: colony collapse disorder • common cold • croup • dengue fever![]() • gastroenteritis • Guillain–Barré syndrome • hepatitis B • hepatitis C • hepatitis E • herpes simplex • HIV/AIDS • influenza
• gastroenteritis • Guillain–Barré syndrome • hepatitis B • hepatitis C • hepatitis E • herpes simplex • HIV/AIDS • influenza![]() • meningitis
• meningitis![]() • myxomatosis • polio
• myxomatosis • polio![]() • pneumonia • shingles • smallpox
• pneumonia • shingles • smallpox
Epidemiology & Interventions: 2007 Bernard Matthews H5N1 outbreak • Coalition for Epidemic Preparedness Innovations • Disease X • 2009 flu pandemic • HIV/AIDS in Malawi • polio vaccine • Spanish flu • West African Ebola virus epidemic
Virus–Host interactions: antibody • host • immune system![]() • parasitism • RNA interference
• parasitism • RNA interference![]()
Methodology: metagenomics
Social & Media: And the Band Played On • Contagion • "Flu Season" • Frank's Cock![]() • Race Against Time: Searching for Hope in AIDS-Ravaged Africa
• Race Against Time: Searching for Hope in AIDS-Ravaged Africa![]() • social history of viruses
• social history of viruses![]() • "Steve Burdick" • "The Time Is Now" • "What Lies Below"
• "Steve Burdick" • "The Time Is Now" • "What Lies Below"
People: Brownie Mary • Macfarlane Burnet![]() • Bobbi Campbell • Aniru Conteh • people with hepatitis C
• Bobbi Campbell • Aniru Conteh • people with hepatitis C![]() • HIV-positive people
• HIV-positive people![]() • Bette Korber • Henrietta Lacks • Linda Laubenstein • Barbara McClintock
• Bette Korber • Henrietta Lacks • Linda Laubenstein • Barbara McClintock![]() • poliomyelitis survivors
• poliomyelitis survivors![]() • Joseph Sonnabend • Eli Todd • Ryan White
• Joseph Sonnabend • Eli Todd • Ryan White![]()
Selected virus
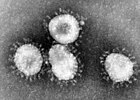
Coronaviruses are a subfamily of RNA viruses in the Nidovirales order which infect mammals and birds. They are spherical enveloped viruses, generally around 80–120 nm in diameter, containing a helical nucleocapsid. Their positive-sense single-stranded RNA genome ranges from approximately 26 to 32 kb in size, one of the largest among RNA viruses. Around 74 characteristic club-shaped spikes project from the envelope, which in electron micrographs resemble the solar corona, from which their name derives. Infectious bronchitis virus was isolated in 1933 from chickens; two mice coronaviruses causing hepatitis and encephalomyelitis were discovered in the 1940s.
Coronaviruses predominantly infect epithelial cells, with the viral spike protein determining tissue tropism and host range. Animal coronaviruses often infect the gastrointestinal tract, causing diarrhoea in cows and pigs, and are transmitted by the faecal–oral route. Human and bird coronaviruses infect the respiratory tract, are transmitted via aerosols and droplets; they cause respiratory tract infections that can range from mild to lethal. Mild illnesses in humans include around 15% of common cold cases, while more lethal coronaviruses cause SARS, MERS and COVID-19. Many human coronaviruses have evolved from viruses of bats.
Did you know?
- ...that Franquet's Epauletted Fruit Bat (pictured) is one of three fruit-eating bats found to be a reservoir for Ebola virus in the wild?
- ...that 95% of adults have been infected by human herpesvirus 7, a virus that can cause influenza-like illness and seizures but normally causes no symptoms?
- ...that James Jurin used statistical studies to show the probability of death from smallpox vaccine was significantly less than from smallpox?
- ...that the log-Cauchy distribution has been proposed as a model for the progression of HIV in individuals?
- ...that Corona, named after Corona, is fighting corona?
Selected biography
Many well-known people have survived the paralytic disease polio. The earliest identified case might be Siptah (pictured), Egyptian pharaoh 1197–1191 BC, whose mummified remains have a deformed leg possibly from polio. Claudius, Roman emperor 41–54 AD, walked with a limp after a childhood disease that historians have hypothesised might have been polio. Novelist Sir Walter Scott suffered paralysis in one leg after a teething fever in 1773, which left him lame; his detailed account of his disease has allowed a retrospective diagnosis of polio to be made with confidence.
For many of those who survived it, paralytic polio was a life-changing experience. The disease can lead to permanent physical disability; Itzhak Perlman, for example, plays the violin seated. Others recover completely, with some going on to excel in sports; Ray Ewry became world's foremost standing jumper after childhood polio. Some survivors, including singer Ian Dury and actress Mia Farrow, have campaigned for polio eradication or for disability rights.
In this month
7 November 1991: Magic Johnson announced his retirement from basketball because of his infection with HIV
14 November 1957: Kuru, the first human prion disease, described by Daniel Gajdusek and Vincent Zigas
16 November 2002: The first case of severe acute respiratory syndrome (virus pictured) recorded in Guangdong, China
17 November 1995: Lamivudine approved for treatment of HIV
22 November 2013: Simeprevir approved for treatment of chronic hepatitis C virus infection
23 November 1978: Structure of tomato bushy stunt virus solved by Stephen Harrison and colleagues, the first atomic-level structure of a virus
24 November 2007: Outbreak of new Ebola species, Bundibugyo virus
26 November 1898: Martinus Beijerinck coined the term contagium vivum fluidum to describe the agent causing tobacco mosaic disease
Selected intervention
Nevirapine (also Viramune) is an antiretroviral drug used in the treatment of HIV/AIDS caused by HIV-1. It was the first non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor to be licensed, which occurred in 1996. Like nucleoside inhibitors, nevirapine inhibits HIV's reverse transcriptase enzyme, which copies the viral RNA into DNA and is essential for its replication. Unlike nucleoside inhibitors, it binds not in the enzyme's active site but in a nearby hydrophobic pocket, causing a conformational change in the enzyme that prevents it from functioning. Mutations in the pocket generate resistance to nevirapine, which develops rapidly unless viral replication is completely suppressed. The drug is therefore only used together with other anti-HIV drugs in combination therapy. The HIV-2 reverse transcriptase has a different pocket structure, rendering it inherently resistant to nevirapine and other first-generation NNRTIs. A single dose of nevirapine is a cost-effective way to reduce mother-to-child transmission of HIV, and has been recommended by the World Health Organization for use in resource-poor settings. Other protocols are recommended in the United States. Rash is the most common adverse event associated with the drug.
Subcategories
Subcategories of virology:
Topics
Things to do
- Comment on what you like and dislike about this portal
- Join the Viruses WikiProject
- Tag articles on viruses and virology with the project banner by adding {{WikiProject Viruses}} to the talk page
- Assess unassessed articles against the project standards
- Create requested pages: red-linked viruses | red-linked virus genera
- Expand a virus stub into a full article, adding images, citations, references and taxoboxes, following the project guidelines
- Create a new article (or expand an old one 5-fold) and nominate it for the main page Did You Know? section
- Improve a B-class article and nominate it for Good Article
 or Featured Article
or Featured Article status
status - Suggest articles, pictures, interesting facts, events and news to be featured here on the portal
WikiProjects & Portals
 WikiProject Viruses
Related WikiProjects
WikiProject Viruses
Related WikiProjects
Medicine • Microbiology • Molecular & Cellular Biology • Veterinary Medicine
Related PortalsAssociated Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
Commons
Free media repository -
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
Wikinews
Free-content news -
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
Wikisource
Free-content library -
Wikispecies
Directory of species -
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus