 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Noxafil, Posanol, others |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a607036 |
| License data |
|
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | By mouth, intravenous |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | Low (8 to 47% Oral) |
| Protein binding | 98 to 99% |
| Metabolism | Liver (glucuronidation) |
| Elimination half-life | 16 to 31 hours |
| Excretion | Fecal (71–77%) and Kidney (13–14%) |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.208.201 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
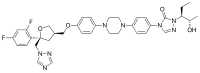
| Formula | C37H42F2N8O4 |
| Molar mass | 700.792 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Posaconazole, sold under the brand name Noxafil among others, is a triazole antifungal medication.[7][8]
It was approved for medical use in the European Union in October 2005,[6] and in the United States in September 2006.[5][9] It is available as a generic medication.[10][11]
- ^ "Posaconazole (Noxafil) Use During Pregnancy". Drugs.com. 23 April 2019. Archived from the original on 30 January 2020. Retrieved 30 January 2020.
- ^ "Posaconazole suspension ARX/Posaconazole TIH/APX-Posaconazole (Arrow Pharma Pty Ltd)". Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA). 16 February 2023. Archived from the original on 18 March 2023. Retrieved 29 April 2023.
- ^ "Posanol Product information". Health Canada. 25 April 2012. Archived from the original on 16 May 2021. Retrieved 3 July 2022.
- ^ "Noxafil 100 mg Gastro-resistant Tablets - Summary of Product Characteristics (SmPC)". (emc). 10 January 2022. Archived from the original on 24 February 2022. Retrieved 3 July 2022.
- ^ a b Cite error: The named reference
Noxafil FDA labelwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ a b "Noxafil EPAR". European Medicines Agency. 28 March 2007. Archived from the original on 19 October 2021. Retrieved 3 July 2022.
- ^ Schiller DS, Fung HB (September 2007). "Posaconazole: an extended-spectrum triazole antifungal agent". Clinical Therapeutics. 29 (9): 1862–86. doi:10.1016/j.clinthera.2007.09.015. PMID 18035188.
- ^ Rachwalski EJ, Wieczorkiewicz JT, Scheetz MH (October 2008). "Posaconazole: an oral triazole with an extended spectrum of activity". The Annals of Pharmacotherapy. 42 (10): 1429–38. doi:10.1345/aph.1L005. PMID 18713852. S2CID 21777822. Retrieved 11 December 2008.[dead link]
- ^ "Drug Approval Package: Noxafil (Posaconazole) NDA #022003". U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). 9 November 2006. Archived from the original on 3 April 2021. Retrieved 15 August 2020.
- ^ "Posaconazole: FDA-Approved Drugs". U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Archived from the original on 20 October 2020. Retrieved 15 August 2020.
- ^ "First Generic Drug Approvals". U.S. Food and Drug Administration. 17 October 2022. Archived from the original on 26 January 2021. Retrieved 28 November 2022.