| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Potassium ferrate(VI)
| |
| Other names
Potassium ferrate
Dipotassium ferrate | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
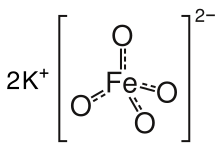
| K2FeO4 | |
| Molar mass | 198.0392 g/mol |
| Appearance | Dark purple solid |
| Density | 2.829 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | >198 °C (decomposes) |
| soluble in 1M KOH | |
| Solubility in other solvents[which?] | reacts with most solvents |
| Structure | |
| K2SO4 motif | |
| Tetrahedral | |
| 0 D | |
| Hazards | |
| Occupational safety and health (OHS/OSH): | |
Main hazards
|
Oxidizer |
| GHS labelling: | |
 [1] [1]
| |
| Danger[1] | |
| H272[1] | |
| P210, P220, P221, P280, P370+P378, P501[1] | |
| Flash point | non-combustible |
| Safety data sheet (SDS) | External SDS |
| Related compounds | |
Other anions
|
K2MnO4 K2CrO4 K2RuO4 |
Other cations
|
BaFeO4 Na2FeO4 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Potassium ferrate is an inorganic compound with the formula K2FeO4. It is the potassium salt of ferric acid. Potassium ferrate is a powerful oxidizing agent with applications in green chemistry, organic synthesis, and cathode technology.
- ^ a b c d "Potassium Ferrate". American Elements. Retrieved June 13, 2019.