 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Probalan |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a682395 |
| Routes of administration | By mouth |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Protein binding | 75-95% |
| Elimination half-life | 2-6 hours (dose: 0.5-1 g) |
| Excretion | kidney (77-88%) |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.313 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
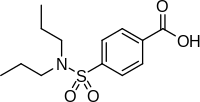
| Formula | C13H19NO4S |
| Molar mass | 285.36 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Probenecid, also sold under the brand name Probalan, is a medication that increases uric acid excretion in the urine. It is primarily used in treating gout and hyperuricemia.
Probenecid was developed as an alternative to caronamide[1] to competitively inhibit renal excretion of some drugs, thereby increasing their plasma concentration and prolonging their effects.
- ^ Mason RM (June 1954). "Studies on the effect of probenecid (benemid) in gout". Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases. 13 (2): 120–130. doi:10.1136/ard.13.2.120. PMC 1030399. PMID 13171805.