| Province ខេត្ត Khétt | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Category | First-level administrative subdivision of a unitary state |
| Location | |
| Number | 25 |
| Populations | 42,665 (Kep) – 2,281,951 (Phnom Penh)[1] |
| Areas | 336 km2 (130 sq mi) (Kep) – 14,288 km2 (5,517 sq mi) (Mondulkiri) |
| Government | |
| Subdivisions | |
| Administrative divisions of Cambodia |
|---|
| First-level |
| Second-level |
| Third-level |
| Fourth-level |
|
| Fifth-level |
|
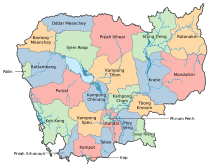
Cambodia is divided into 25 provinces (Khmer: ខេត្ត, khétt [kʰaet]). The capital Phnom Penh is not a province but an "autonomous municipality" (Khmer: រាជធានី, réachthéani [riəceaʔtʰiəniː]; lit. 'capital'), equivalent to a province governmentally and administered at the same level as the other 24 provinces.
Phnom Penh has both the highest population and the highest population density of all provinces, but is the second smallest in land area. The largest province by area is Mondulkiri and the smallest is Kep which is also the least populated province. Mondulkiri has the lowest population density.
Each province is administered by a governor, who is nominated by the Ministry of Interior, subject to approval by the Prime Minister.
Provinces are divided into districts (ស្រុក, srŏk). The districts in Phnom Penh are called khan (ខណ្ឌ) normally written as for addresses in English followed by the districts' names (Ex: Khan Chamkar Mon; lit. 'Chamkar Mon District'). The number of districts in each province varies, from two in the smallest provinces to 14 in Battambang, Prey Veng, and Siem Reap. Further subdivision levels are communes (ឃុំ khum), and further subdivided into villages (ភូមិ, phum). In Phnom Penh, sangkat (សង្កាត់) is used in the place of khum and, similar to khan, normally preferred for writing addresses in English (Ex: Sangkat Mittapheap; lit. 'Mittapheap Commune').