| Flying fox Temporal range:
| |
|---|---|

| |
| Gray-headed flying fox | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Chiroptera |
| Family: | Pteropodidae |
| Subfamily: | Pteropodinae |
| Genus: | Pteropus Brisson, 1762 |
| Type species | |
| Vespertilio vampyrus niger[2] Kerr, 1792
| |
| |
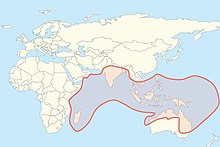
| Worldwide distribution of flying foxes | |
Pteropus (suborder Yinpterochiroptera) is a genus of megabats which are among the largest bats in the world. They are commonly known as fruit bats or flying foxes, among other colloquial names. They live in South Asia, Southeast Asia, Australia, East Africa, and some oceanic islands in the Indian and Pacific Oceans.[3] There are at least 60 extant species in the genus.[4]
Flying foxes eat fruit and other plant matter, and occasionally consume insects as well. They locate resources with their keen sense of smell. Most, but not all, are nocturnal. They navigate with keen eyesight, as they cannot echolocate. They have long life spans and low reproductive outputs, with females of most species producing only one offspring per year. Their slow life history makes their populations vulnerable to threats such as overhunting, culling, and natural disasters. Six flying fox species have been made extinct in modern times by overhunting. Flying foxes are often persecuted for their real or perceived role in damaging crops. They are ecologically beneficial by assisting in the regeneration of forests via seed dispersal. They benefit ecosystems and human interests by pollinating plants.
Like other bats, flying foxes are relevant to humans as a source of disease, as they are the reservoirs of rare but fatal disease agents including Australian bat lyssavirus, which causes rabies, and Hendra virus; seven known human deaths have resulted from these two diseases. Nipah virus is also transmitted by flying foxes—it affects more people, with over 100 attributed fatalities. They have cultural significance to indigenous people, with appearances in traditional art, folklore, and weaponry. Their fur and teeth were used as currency in the past. Some cultures still use their teeth as currency today.
- ^ "Pteropus Brisson 1762 (flying fox)". Fossilworks. Archived from the original on 12 March 2023. Retrieved 17 December 2021.
- ^ ICZN (1998). "Opinion 1894. Regnum Animale ..., Ed. 2 (M.J. Brisson, 1762): rejected for nomenclatural purposes, with the conservation of the mammalian generic names Philander (Marsupialia), Pteropus (Chiroptera), Glis, Cuniculus, and Hydrochoerus (Rodentia), Meles, Lutra and Hyaena (Carnivora), Tapirus (Perissodactyla), Tragulus and Giraffa (Artiodactyla)". Bulletin of Zoological Nomenclature. 55 (1): 64–71.
- ^ Nowak, R. M., ed. (1999). Walker's Mammals of the World. Vol. 1 (6 ed.). Johns Hopkins University Press. pp. 264–271. ISBN 978-0-8018-5789-8.
- ^ Simmons, N.B. (2005). "Genus Pteropus". In Wilson, D.E.; Reeder, D.M (eds.). Mammal Species of the World: A Taxonomic and Geographic Reference (3rd ed.). Johns Hopkins University Press. pp. 334–346. ISBN 978-0-8018-8221-0. OCLC 62265494.