| Pulmonary valve stenosis | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Valvular pulmonary stenosis[1] |
 | |
| Specialty | Cardiology |
| Symptoms | Cyanosis, dizziness[2] |
| Causes | Congenital (most often)[3] |
| Diagnostic method | Echocardiogram, Ultrasound[4] |
| Treatment | Valve replacement or surgical repair |
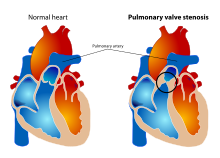
Pulmonary valve stenosis (PVS) is a heart valve disorder. Blood going from the heart to the lungs goes through the pulmonary valve, whose purpose is to prevent blood from flowing back to the heart. In pulmonary valve stenosis this opening is too narrow, leading to a reduction of flow of blood to the lungs.[1][5]
While the most common cause of pulmonary valve stenosis is congenital heart disease, it may also be due to a malignant carcinoid tumor. Both stenosis of the pulmonary artery and pulmonary valve stenosis are forms of pulmonic stenosis (nonvalvular and valvular, respectively)[6] but pulmonary valve stenosis accounts for 80% of pulmonic stenosis. PVS was the key finding that led Jacqueline Noonan to identify the syndrome now called Noonan syndrome.
- ^ a b "Pulmonary valve stenosis: MedlinePlus Medical Encyclopedia". www.nlm.nih.gov. Archived from the original on 2016-07-05. Retrieved 2015-11-18.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
emedicinewas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Cite error: The named reference
valwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ "Pulmonary Valve Disease. About Pulmonary valve disease | Patient". Patient. Archived from the original on 2020-04-05. Retrieved 2015-11-18.
- ^ Choices, NHS. "Congenital heart disease - Types - NHS Choices". www.nhs.uk. Archived from the original on 2017-09-20. Retrieved 2015-11-18.
- ^ Ren, XM; et al. (2014-12-23), "Pulmonic stenosis", Medscape, archived from the original on 2016-03-14, retrieved 2016-03-10.