| |||
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
1H-Pyrazole[1] | |||
| Systematic IUPAC name
1,2-Diazacyclopenta-2,4-diene | |||
| Other names
1,2-Diazole
| |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| 103775 | |||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChEMBL | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| DrugBank | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.005.471 | ||
| EC Number |
| ||
| 1360 | |||
| KEGG | |||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| UNII | |||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C3H4N2 | |||
| Molar mass | 68.079 g·mol−1 | ||
| Melting point | 66 to 70 °C (151 to 158 °F; 339 to 343 K) | ||
| Boiling point | 186 to 188 °C (367 to 370 °F; 459 to 461 K) | ||
| Basicity (pKb) | 11.5 | ||
| Hazards | |||
| GHS labelling:[2] | |||
   
| |||
| Danger | |||
| H302, H311, H315, H318, H319, H335, H372, H412 | |||
| P260, P261, P262, P264, P264+P265, P270, P271, P273, P280, P301+P317, P302+P352, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P305+P354+P338, P316, P317, P319, P321, P330, P332+P317, P337+P317, P361+P364, P362+P364, P403+P233, P405, P501 | |||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |||
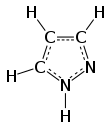
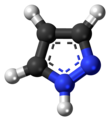
Pyrazole is an organic compound with the formula (CH)3N2H. It is a heterocycle characterized as an azole with a 5-membered ring of three carbon atoms and two adjacent nitrogen atoms, which are in ortho-substitution. Pyrazole itself has few applications but many substituted pyrazoles are of commercial interest.
- ^ "Front Matter". Nomenclature of Organic Chemistry : IUPAC Recommendations and Preferred Names 2013 (Blue Book). Cambridge: The Royal Society of Chemistry. 2014. p. 141. doi:10.1039/9781849733069-FP001. ISBN 978-0-85404-182-4.
- ^ "Pyrazole". pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov. Retrieved 17 February 2024.