| Pyruvate decarboxylase | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
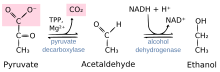 Reaction catalyzed by pyruvate decarboxylase: pyruvate + thiamine pyrophosphate (TPP) → hydroxyethyl-TPP + CO2 | |||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||
| EC no. | 4.1.1.1 | ||||||||
| CAS no. | 9001-04-1 | ||||||||
| Databases | |||||||||
| IntEnz | IntEnz view | ||||||||
| BRENDA | BRENDA entry | ||||||||
| ExPASy | NiceZyme view | ||||||||
| KEGG | KEGG entry | ||||||||
| MetaCyc | metabolic pathway | ||||||||
| PRIAM | profile | ||||||||
| PDB structures | RCSB PDB PDBe PDBsum | ||||||||
| Gene Ontology | AmiGO / QuickGO | ||||||||
| |||||||||
Pyruvate decarboxylase is an enzyme (EC 4.1.1.1) that catalyses the decarboxylation of pyruvic acid to acetaldehyde. It is also called 2-oxo-acid carboxylase, alpha-ketoacid carboxylase, and pyruvic decarboxylase.[1] In anaerobic conditions, this enzyme participates in the fermentation process that occurs in yeast, especially of the genus Saccharomyces, to produce ethanol by fermentation. It is also present in some species of fish (including goldfish and carp) where it permits the fish to perform ethanol fermentation (along with lactic acid fermentation) when oxygen is scarce.[2] Pyruvate decarboxylase starts this process by converting pyruvate into acetaldehyde and carbon dioxide.[3] Pyruvate decarboxylase depends on cofactors thiamine pyrophosphate (TPP) and magnesium. This enzyme should not be mistaken for the unrelated enzyme pyruvate dehydrogenase, an oxidoreductase (EC 1.2.4.1), that catalyzes the oxidative decarboxylation of pyruvate to acetyl-CoA.
- ^ "NiceZyme View of ENZYME: EC 4.1.1.1". ExPASy Proteomics Server.
- ^ Aren van Waarde; G. Van den Thillart; Maria Verhagen (1993). "Ethanol Formation and pH-Regulation in Fish". Surviving Hypoxia. CRC Press. pp. 157−170. hdl:11370/3196a88e-a978-4293-8f6f-cd6876d8c428. ISBN 0-8493-4226-0.
- ^ Tadhg P. Begley; McMurry, John (2005). The organic chemistry of biological pathways. Roberts and Co. Publishers. p. 179. ISBN 0-9747077-1-6.