| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Pronunciation | /ˈkwɜːrsɪtɪn/ |
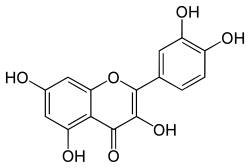
| IUPAC name
3,3′,4′,5,7-Pentahydroxyflavone
| |
| Systematic IUPAC name
2-(3,4-Dihydroxyphenyl)-3,5,7-trihydroxy-4H-1-benzopyran-4-one | |
| Other names
5,7,3′,4′-flavon-3-ol, Sophoretin, Meletin, Quercetine, Xanthaurine, Quercetol, Quercitin, Quertine, Flavin meletin
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| 317313 | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| DrugBank | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.003.807 |
| EC Number |
|
| 579210 | |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII |
|
| UN number | 2811 |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C15H10O7 | |
| Molar mass | 302.236 g/mol |
| Appearance | yellow crystalline powder[1] |
| Density | 1.799 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 316 °C (601 °F; 589 K) |
| Practically insoluble in water; soluble in aqueous alkaline solutions[1] | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |

Quercetin is a plant flavonol from the flavonoid group of polyphenols. It is found in many fruits, vegetables, leaves, seeds, and grains; capers, red onions, and kale are common foods containing appreciable amounts of it.[2][3] It has a bitter flavor and is used as an ingredient in dietary supplements, beverages, and foods.
- ^ a b c "Quercetin dihydrate safety sheet". Archived from the original on September 16, 2011.
- ^ "Flavonoids". Micronutrient Information Center, Linus Pauling Institute, Oregon State University, Corvallis, OR. November 2015. Retrieved 1 April 2018.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
usdawas invoked but never defined (see the help page).