This article needs additional citations for verification. (April 2015) |
| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
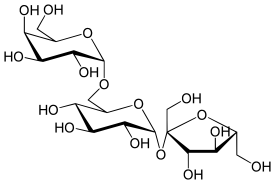
| IUPAC name
β-D-Fructofuranosyl α-D-galactopyranosyl-(1→6)-α-D-glucopyranoside
| |
| Systematic IUPAC name
(2R,3R,4S,5S,6R)-2-{[(2S,3S,4S,5R)-3,4-Dihydroxy-2,5-bis(hydroxymethyl)oxolan-2-yl]oxy}-6-({[(2S,3R,4S,5R,6R)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)oxan-2-yl]oxy}methyl)oxane-3,4,5-triol | |
| Other names
rafinosa
D-(+)-Raffinose D-Raffinose D-raffinose pentahydrate Gossypose Melitose Melitriose NSC 170228 NSC 2025 6G-α-D-galactosylsucrose; β-D-fructofuranosyl-O-α-D-glucopyranosyl-(1→6)-α-D-galactopyranoside hydrate(1:5) | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.007.407 |
| EC Number |
|
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C18H32O16 | |
| Molar mass | 594.5 g/mol (pentahydrate) |
| Melting point | 118 °C |
| 203 g/L | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Raffinose is a trisaccharide composed of galactose, glucose, and fructose. It can be found in beans, cabbage, brussels sprouts, broccoli, asparagus, other vegetables, and whole grains. Raffinose can be hydrolyzed to D-galactose and sucrose by the enzyme α-galactosidase (α-GAL), an enzyme synthesized by bacteria found in the large intestine. α-GAL also hydrolyzes other α-galactosides such as stachyose, verbascose, and galactinol, if present. In plants, raffinose plays a significant role in stress responses, particularly temperature sensitivity, seed vigour, resistance to pathogens, and desiccation.