| Rail transport in Lithuania | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 Train near Vilnius | |||||
| Operation | |||||
| National railway | Lietuvos Geležinkeliai (LTG) | ||||
| Statistics | |||||
| Ridership | 5.5 million (2019)[1] | ||||
| Passenger km | 359 million (2019)[2] | ||||
| Freight | 16,181 million tkm (2019)[2] | ||||
| System length | |||||
| Total | 1,910 km (1,190 mi) | ||||
| Double track | 459 km (285 mi)[3] | ||||
| Electrified | 156 km (97 mi)[3] | ||||
| Track gauge | |||||
| Main | 1,520 mm (4 ft 11+27⁄32 in) 1,435 mm (4 ft 8+1⁄2 in) | ||||
| 1520 mm | 1,745.8 km (1,084.8 mi) | ||||
| 1435 mm | 123 km (76 mi) | ||||
| 750 mm | 68.4 km (42.5 mi) | ||||
| Electrification | |||||
| Main | 25 kV AC, 50 Hz | ||||
| Features | |||||
| Longest tunnel | Kaunas Railway Tunnel, 1,285 m (4,216 ft) | ||||
| No. bridges | 410[4] | ||||
| Longest bridge | Lyduvėnai Bridge, 599 m (1,965 ft)[5] | ||||
| No. stations | 104[4] (or 164 if including all stops)[3] | ||||
| |||||
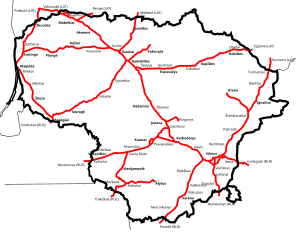
Rail transport in Lithuania consists of freight shipments and passenger services. The construction of the first railway line in Lithuania began in 1859. As of 2021[update], the total length of railways in Lithuania was 1,868.8 km (1,161.2 mi). LTG Group (Lietuvos Geležinkeliai), the national state-owned railway company, operates most of the country's passenger and freight services via its subsidiaries LTG Link (passenger) and LTG Cargo (freight).
The country has a mixed gauge network: the majority is broad gauge (a legacy of the Russian standard) with new lines often using standard gauge or dual gauge track. In 2020, Lithuania together with the other Baltic states began construction of the Rail Baltica high-speed rail with operating speed of 249 km/h for the passenger trains. The project marks a new era for Lithuanian railways and is expected to be completed by 2030.
Lithuania is a member of the Intergovernmental Organisation for International Carriage by Rail (OTIF) and International Union of Railways (UIC). The UIC Country Code for Lithuania is 24. As an EU member, the country participates in the European Union Agency for Railways. It is also a member of Interrail and Eurail. Lithuania was ranked 16th among national European rail systems in the European Railway Performance Index 2017 assessing intensity of use, quality of service and safety.[6]
- ^ "AB "Lietuvos geležinkeliai" 2020 Metinė ataskaita" (PDF) (in Lithuanian). Lietuvos geležinkeliai. Archived from the original on 16 October 2021. Retrieved 16 October 2021.
- ^ a b "Country Profile – Lithuania". United Nations Economic Commission for Europe. Retrieved 2 October 2021.
- ^ a b c Cite error: The named reference
ltg-infra-paramswas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ a b Cite error: The named reference
vle-railway-historywas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ "LTG Infra seeks contractor to construct longest railway bridge in the Baltic region". Railway Technology. 29 December 2020. Archived from the original on 27 January 2021. Retrieved 10 October 2021.
- ^ "The 2017 European Railway Performance Index". Boston Consulting Group. 8 January 2021. Archived from the original on 16 October 2021.