The random phase approximation (RPA) is an approximation method in condensed matter physics and in nuclear physics. It was first introduced by David Bohm and David Pines as an important result in a series of seminal papers of 1952 and 1953.[1][2][3] For decades physicists had been trying to incorporate the effect of microscopic quantum mechanical interactions between electrons in the theory of matter. Bohm and Pines' RPA accounts for the weak screened Coulomb interaction and is commonly used for describing the dynamic linear electronic response of electron systems. It was further developed to the relativistic form (RRPA) by solving the Dirac equation.[4][5]
In the RPA, electrons are assumed to respond only to the total electric potential V(r) which is the sum of the external perturbing potential Vext(r) and a screening potential Vsc(r). The external perturbing potential is assumed to oscillate at a single frequency ω, so that the model yields via a self-consistent field (SCF) method [6] a dynamic dielectric function denoted by εRPA(k, ω).
The contribution to the dielectric function from the total electric potential is assumed to average out, so that only the potential at wave vector k contributes. This is what is meant by the random phase approximation. The resulting dielectric function, also called the Lindhard dielectric function,[7][8] correctly predicts a number of properties of the electron gas, including plasmons.[9]
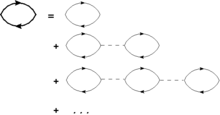
The RPA was criticized in the late 1950s for overcounting the degrees of freedom and the call for justification led to intense work among theoretical physicists. In a seminal paper Murray Gell-Mann and Keith Brueckner showed that the RPA can be derived from a summation of leading-order chain Feynman diagrams in a dense electron gas.[10]
The consistency in these results became an important justification and motivated a very strong growth in theoretical physics in the late 50s and 60s.
- ^ Bohm, David; Pines, David (1 May 1951). "A Collective Description of Electron Interactions. I. Magnetic Interactions". Physical Review. 82 (5). American Physical Society (APS): 625–634. Bibcode:1951PhRv...82..625B. doi:10.1103/physrev.82.625. ISSN 0031-899X.
- ^ Pines, David; Bohm, David (15 January 1952). "A Collective Description of Electron Interactions: II. CollectivevsIndividual Particle Aspects of the Interactions". Physical Review. 85 (2). American Physical Society (APS): 338–353. Bibcode:1952PhRv...85..338P. doi:10.1103/physrev.85.338. ISSN 0031-899X.
- ^ Bohm, David; Pines, David (1 October 1953). "A Collective Description of Electron Interactions: III. Coulomb Interactions in a Degenerate Electron Gas". Physical Review. 92 (3). American Physical Society (APS): 609–625. Bibcode:1953PhRv...92..609B. doi:10.1103/physrev.92.609. ISSN 0031-899X.
- ^ Deshmukh, Pranawa C.; Manson, Steven T. (September 2022). "Photoionization of Atomic Systems Using the Random-Phase Approximation Including Relativistic Interactions". Atoms. 10 (3): 71. Bibcode:2022Atoms..10...71D. doi:10.3390/atoms10030071. ISSN 2218-2004.
- ^ Johnson, W R; Lin, C D; Cheng, K T; Lee, C M (1980-01-01). "Relativistic Random-Phase Approximation". Physica Scripta. 21 (3–4): 409–422. Bibcode:1980PhyS...21..409J. doi:10.1088/0031-8949/21/3-4/029. ISSN 0031-8949. S2CID 94058089.
- ^ Ehrenreich, H.; Cohen, M. H. (15 August 1959). "Self-Consistent Field Approach to the Many-Electron Problem". Physical Review. 115 (4). American Physical Society (APS): 786–790. Bibcode:1959PhRv..115..786E. doi:10.1103/physrev.115.786. ISSN 0031-899X.
- ^ J. Lindhard (1954). "On the Properties of a Gas of Charged Particles" (PDF). Kongelige Danske Videnskabernes Selskab, Matematisk-Fysiske Meddelelser. 28 (8).
- ^ N. W. Ashcroft and N. D. Mermin, Solid State Physics (Thomson Learning, Toronto, 1976)
- ^ G. D. Mahan, Many-Particle Physics, 2nd ed. (Plenum Press, New York, 1990)
- ^ Gell-Mann, Murray; Brueckner, Keith A. (15 April 1957). "Correlation Energy of an Electron Gas at High Density" (PDF). Physical Review. 106 (2). American Physical Society (APS): 364–368. Bibcode:1957PhRv..106..364G. doi:10.1103/physrev.106.364. ISSN 0031-899X. S2CID 120701027.