This article has multiple issues. Please help improve it or discuss these issues on the talk page. (Learn how and when to remove these messages)
|
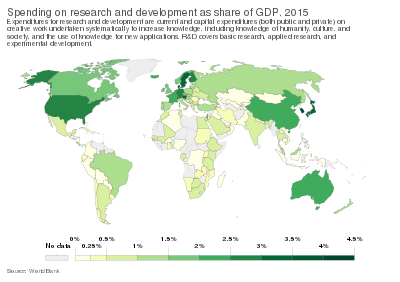
Research and development (R&D or R+D)[1] is the set of innovative activities undertaken by corporations or governments in developing new services or products.[2][3][4] R&D constitutes the first stage of development of a potential new service or the production process.
Although R&D activities may differ across businesses, the primary goal of an R&D department is to develop new products and services.[2][4] R&D differs from the vast majority of corporate activities in that it is not intended to yield immediate profit, and generally carries greater risk and an uncertain return on investment.[2][5] R&D is crucial for acquiring larger shares of the market through new products.[4] R&D&I represents R&D with innovation.[6][7][8]
- ^ "Policy for research and technological development | Fact Sheets on the European Union | European Parliament". 31 March 2023.
- ^ a b c "Research and Development in the Pharmaceutical Industry". US Congressional Budget Office. April 2021. Retrieved 29 August 2024.
- ^ Wragg, David W. (1973). A Dictionary of Aviation (first ed.). Osprey. p. 223. ISBN 9780850451634.
- ^ a b c Staff, Investopedia (2003-11-25). "Research And Development – R&D". Investopedia. Retrieved 2017-12-12.
- ^ Yiu, L. M. Daphne; Lam, Hugo K. S.; Yeung, Andy C. L.; Cheng, T. C. E. (2020). "Enhancing the Financial Returns of R&D Investments through Operations Management". Production and Operations Management. 29 (7): 1658–1678. doi:10.1111/poms.13186. hdl:10397/89881. ISSN 1937-5956. S2CID 216529963.
- ^ EUROPEAN COMMISSION https://ec.europa.eu/competition/state_aid/cases/220403/220403_758165_5_1.pdf
- ^ Expenses for university R&D&I increase moderately in Spain https://www.eurekalert.org/pub_releases/2021-07/ucid-efu072221.php
- ^ Research, Development and Innovation (R&D&I), Fundação Para a Ciência e Tecnologia https://www.fct.pt/dsi/idi/index.phtml.en