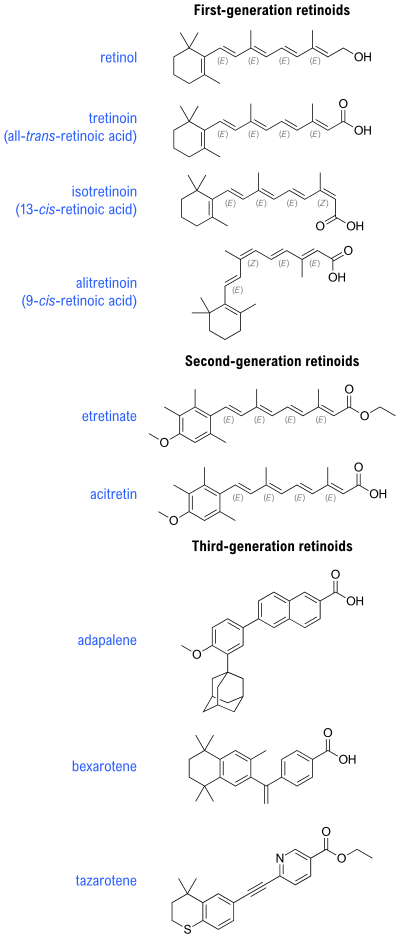
The retinoids are a class of chemical compounds that are natural derivatives of vitamin A or are chemically related to it. Synthetic retinoids are used in medicine where they regulate skin health, immunity and bone disorders.
Retinoids have many important functions throughout the body, including roles in vision,[1] regulation of skin proliferation and differentiation, growth of bone tissue, immune function,[2] and male fertility.[3]
The biology of retinoids is complex and their use in medicine has well-known benefits in diseases like acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL) or acne. On the other hand, retinoids are known to have many harmful effects on metabolism[4] and cancer.[5]
- ^ Kiser PD, Golczak M, Palczewski K (January 2014). "Chemistry of the retinoid (visual) cycle". Chemical Reviews. 114 (1): 194–232. doi:10.1021/cr400107q. PMC 3858459. PMID 23905688.

- ^ Hall JA, Grainger JR, Spencer SP, Belkaid Y (July 2011). "The role of retinoic acid in tolerance and immunity". Immunity. 35 (1): 13–22. doi:10.1016/j.immuni.2011.07.002. PMC 3418663. PMID 21777796.
- ^ Topping T, Griswold MD (2022-04-28). "Global Deletion of ALDH1A1 and ALDH1A2 Genes Does Not Affect Viability but Blocks Spermatogenesis". Frontiers in Endocrinology. 13: 871225. doi:10.3389/fendo.2022.871225. PMC 9097449. PMID 35574006.
- ^ Esposito M, Amory JK, Kang Y (September 2024). "The pathogenic role of retinoid nuclear receptor signaling in cancer and metabolic syndromes". The Journal of Experimental Medicine. 221 (9): e20240519. doi:10.1084/jem.20240519. PMC 11318670. PMID 39133222.
- ^ Goodman GE, Thornquist MD, Balmes J, Cullen MR, Meyskens FL, Omenn GS, et al. (December 2004). "The Beta-Carotene and Retinol Efficacy Trial: incidence of lung cancer and cardiovascular disease mortality during 6-year follow-up after stopping beta-carotene and retinol supplements". Journal of the National Cancer Institute. 96 (23): 1743–1750. doi:10.1093/jnci/djh320. PMID 15572756.