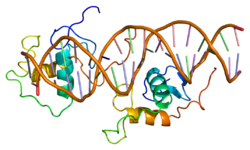
Rev-Erb alpha (Rev-Erbɑ), also known as nuclear receptor subfamily 1 group D member 1 (NR1D1), is one of two Rev-Erb proteins in the nuclear receptor (NR) family of intracellular transcription factors. In humans, REV-ERBɑ is encoded by the NR1D1 gene, which is highly conserved across animal species.[5]
Rev-Erbɑ plays an important role in regulation of the core circadian clock through repression of the positive clock element Bmal1. It also regulates several physiological processes under circadian control, including metabolic and immune pathways.[6][7] Rev-Erbɑ mRNA demonstrates circadian oscillation in its expression, and it is highly expressed in mammals in the brain and metabolic tissues such as skeletal muscle, adipose tissue, and liver.[6][8]
- ^ a b c GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000126368 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ a b c GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000020889 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ "NR1D1 Gene | NR1D1 Protein | NR1D1 Antibody". GeneCards. Retrieved 2021-05-06.
- ^ a b Yin L, Wu N, Lazar MA (April 2010). "Nuclear receptor Rev-erbalpha: a heme receptor that coordinates circadian rhythm and metabolism". Nuclear Receptor Signaling. 8 (1): e001. doi:10.1621/nrs.08001. PMC 2858265. PMID 20414452.
- ^ Wang S, Li F, Lin Y, Wu B (2020). "Targeting REV-ERBα for therapeutic purposes: promises and challenges". Theranostics. 10 (9): 4168–4182. doi:10.7150/thno.43834. PMC 7086371. PMID 32226546.
- ^ Burris TP (July 2008). "Nuclear hormone receptors for heme: REV-ERBalpha and REV-ERBbeta are ligand-regulated components of the mammalian clock". Molecular Endocrinology. 22 (7): 1509–20. doi:10.1210/me.2007-0519. PMC 5419435. PMID 18218725.