| History of geography |
|---|
 |
 |
|---|
| Periods |
|
| Constitution |
| Political institutions |
| Assemblies |
| Ordinary magistrates |
| Extraordinary magistrates |
| Public law |
| Senatus consultum ultimum |
| Titles and honours |
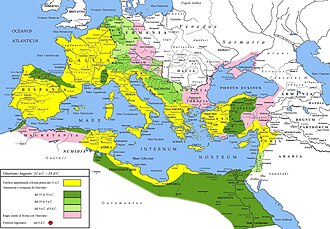

The Roman provinces (Latin: provincia, pl. provinciae) were the administrative regions of Ancient Rome outside Roman Italy that were controlled by the Romans under the Roman Republic and later the Roman Empire. Each province was ruled by a Roman appointed as governor.[1]
For centuries, it was the largest administrative unit of the foreign possessions of ancient Rome.[1] With the administrative reform initiated by Diocletian, it became a third level administrative subdivision of the Roman Empire, or rather a subdivision of the imperial dioceses (in turn subdivisions of the imperial prefectures).[1]
- ^ a b c "Le province romane" (in Italian). Retrieved 20 November 2021.