 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Pronunciation | /ruːˈkæpərɪb/ roo-KAP-ər-ib |
| Trade names | Rubraca |
| Other names | CO-338, AG-014699, PF-0136738, PF-01367338 |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a617002 |
| License data | |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | By mouth |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 30–45% (Tmax = 1.9 hours) |
| Protein binding | 70% (in vitro) |
| Metabolism | Liver (primarily CYP2D6; 1A2 and 3A4 to a lesser extent) |
| Elimination half-life | 17–19 hours[2] |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number |
|
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII |
|
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI |
|
| ChEMBL |
|
| PDB ligand | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.247.490 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
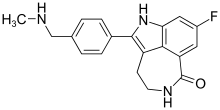
| Formula | C19H18FN3O |
| Molar mass | 323.371 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Rucaparib, sold under the brand name Rubraca, is a PARP inhibitor used as an anti-cancer agent.[2] Rucaparib is a first-in-class pharmaceutical drug targeting the DNA repair enzyme poly-ADP ribose polymerase-1 (PARP-1). It is taken by mouth.[2][4]
The most common side effects include tiredness or weakness, nausea (feeling sick), increased levels of creatinine (which may indicate kidney problems) and liver enzymes in the blood (which may indicate liver damage), vomiting, anaemia (low red blood cell counts), decreased appetite, dysgeusia (taste disturbances), diarrhoea, thrombocytopenia (low levels of platelets) and abdominal pain (belly ache).[3][2]
- ^ "Rubraca 200mg film-coated tablets - Summary of Product Characteristics (SmPC)". (emc). 19 June 2019. Archived from the original on 29 August 2021. Retrieved 17 May 2020.
- ^ a b c d e "Rubraca- rucaparib tablet, film coated". DailyMed. 6 April 2018. Archived from the original on 9 May 2020. Retrieved 17 May 2020.
- ^ a b Cite error: The named reference
Rubraca EPARwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ "Cancer Research Launches New Drug Trial". netdoctor.co.uk. Hearst Magazines UK. 10 January 2012. Archived from the original on 26 December 2017. Retrieved 20 December 2016.