| IEC 61966-2-1 Default RGB Colour Space - sRGB | |
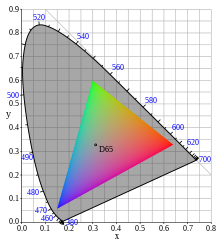 sRGB colors situated at calculated position in CIE 1931 chromaticity diagram. Luminance set so that to avoid mach bands. | |
| Abbreviation | sRGB |
|---|---|
| Status | Published |
| Year started | 1996 |
| First published | October 18, 1999[1] |
| Organization | IEC[1] |
| Committee | TC/SC: TC 100/TA 2[1] |
| Base standards | IEC 61966 Colour Measurement and Management in Multimedia Systems and Equipment |
| Domain | Color space, color model |
| Website | webstore |
sRGB is a standard RGB (red, green, blue) color space that HP and Microsoft created cooperatively in 1996 to use on monitors, printers, and the World Wide Web.[2] It was subsequently standardized by the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) as IEC 61966-2-1:1999.[1] sRGB is the current defined standard colorspace for the web, and it is usually the assumed colorspace for images that are neither tagged for a colorspace nor have an embedded color profile.
sRGB essentially codifies the display specifications for the computer monitors in use at that time, which greatly aided its acceptance. sRGB uses the same color primaries and white point as ITU-R BT.709 standard for HDTV,[3] a transfer function (or gamma) compatible with the era's CRT displays, and a viewing environment designed to match typical home and office viewing conditions.
- ^ a b c d "IEC 61966-2-1:1999". IEC Webstore. International Electrotechnical Commission. Retrieved 3 March 2017.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
orig_pubwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Charles A. Poynton (2003). Digital Video and HDTV: Algorithms and Interfaces. Morgan Kaufmann. ISBN 1-55860-792-7.

