| Observation data Epoch J2000 Equinox J2000 | |
|---|---|
| Constellation | Sagittarius |
| Right ascension | 17h 45m 40.0409s [1] |
| Declination | −29° 00′ 28.118″ [1] |
| Astrometry | |
| Radial velocity (Rv) | 46 km/s |
| Details | |
| Mass | ~4.1 million M☉ |
| Radius | 31.6 R☉ |
| Age | +10.000 years |
| Other designations | |
AX J1745.6-2900, SAGITTARIUS A, W 24, Cul 1742-28, SGR A, [DGW65] 96, EQ 1742-28, RORF 1742-289, [SKM2002] 28. | |
| Database references | |
| SIMBAD | data |
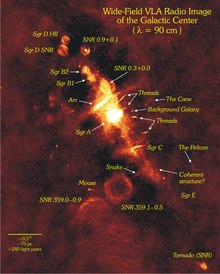
Sagittarius A (Sgr A) is a complex radio source at the center of the Milky Way, which contains a supermassive black hole. It is located between Scorpius and Sagittarius, and is hidden from view at optical wavelengths by large clouds of cosmic dust in the spiral arms of the Milky Way. The dust lane that obscures the Galactic Center from a vantage point around the Sun causes the Great Rift through the bright bulge of the galaxy.
The radio source consists of three components: the supernova remnant Sagittarius A East, the spiral structure Sagittarius A West, and a very bright compact radio source at the center of the spiral, Sagittarius A* (read "A-star"). These three overlap: Sagittarius A East is the largest, West appears off-center within East, and A* is at the center of West.