Charlotte Amalie in Saint Thomas in December 2013 | |
| Geography | |
|---|---|
| Location | Caribbean Sea |
| Coordinates | 18°20′N 64°55′W / 18.333°N 64.917°W |
| Archipelago | Virgin Islands, Leeward Islands |
| Area | 32 sq mi (83 km2) |
| Highest elevation | 1,555 ft (474 m) |
| Highest point | Crown Mountain[1] |
| Administration | |
| Insular area | |
| Largest settlement | Charlotte Amalie (pop. 14,477) |
| Administrator | Avery Lewis |
| Demographics | |
| Population | 42,261 (2020 census[2]) |
| Pop. density | 509.2/km2 (1318.8/sq mi) |
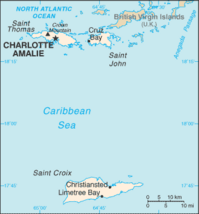
Saint Thomas (Danish: Sankt Thomas, Spanish: Santo Tomás, French: Saint-Thomas) is one of the Virgin Islands in the Caribbean Sea, and a constituent district of the United States Virgin Islands (USVI), an unincorporated territory of the United States. Along with surrounding minor islands, it is one of three county-equivalents in the USVI. Together with Saint John, it forms one of the districts of the USVI. The territorial capital and port of Charlotte Amalie is located on the island.
Of the three islands, St. Thomas is the second-largest, with St. Croix being the largest, and St. John, the smallest.[3] As of the 2020 census, the population of Saint Thomas was 42,261,[4] about 48.5% of the total population of the United States Virgin Islands. Crown Mountain is the highest point in Saint Thomas and in the entire United States Virgin Islands. Hence, it is called "Rock City".[5] The island has a land area of 32 square miles (83 km2).[6]
- ^ "Where is the U.S. Virgin Islands: Geography". vinow.com. Retrieved April 8, 2017.
- ^ "2020 Island Areas Censuses: U.S. Virgin Islands". US Census Bureau. Retrieved December 1, 2022.
- ^ "What Are the US Virgin Islands: USVI 101". Sea Glass Properties. May 22, 2023. Retrieved March 16, 2024.
- ^ "2020 Island Areas Censuses: U.S. Virgin Islands". US Census Bureau. Retrieved December 1, 2022.
- ^ Connor Jr., Sean (December 29, 2017). "Don't Forget the Capital". St. Thomas Source. Retrieved March 16, 2024.
- ^ This is the figure given on page 1 of the United States Geological Survey's Open-File Report 72-201. It is also the figure given in the article at the on-line edition of the Encyclopedia Britannica. The Virgin Islands (United States) page Archived March 10, 2019, at the Wayback Machine at the United Nations Environmental Programme's Island Directory gives a substantially lower figure, reporting the area as 69.7 square kilometers, equivalent to 26.9 square miles. And although the U.S. Census Bureau does not report the areas of geographic entities, it does report their population densities (equal to the total population divided by the area). In the 2010 census, the population was reported as 51,634 (Table P1, "Total Population") and the population density was reported as 1,649.1 per square mile (Table P40, "Population Density"). Together, these figures imply an area of 31.3 square miles.