| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
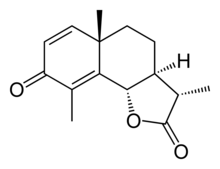
| IUPAC name
(11S)-6α,12-Epoxyeudesma-1,4-diene-3,12-dione
| |
| Systematic IUPAC name
(3S,3aS,5aS,9bS)-3,5a,9-Trimethyl-3a,5,5a,9b-tetrahydronaphtho[1,2-b]furan-2,8(3H,4H)-dione | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.006.874 |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C15H18O3 | |
| Molar mass | 246.30162 |
| Melting point | 172 °C (342 °F; 445 K) |
| Boiling point | 423 °C (793 °F; 696 K) |
| insoluble | |
| Vapor pressure | 1*10−7mmHg |
| Hazards | |
| Flash point | 190 °C (374 °F; 463 K) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Santonin is a drug which was widely used in the past as an anthelminthic. It is an organic compound consisting of colorless flat prisms, turning slightly yellow from the action of light and soluble in alcohol, chloroform and boiling water.
According to the US Pharmacopoeia, santonin occurs "in colorless, shining, flattened, prismatic crystals, odorless and nearly tasteless when first put in the mouth, but afterward developing a bitter taste; not altered by exposure to air, but turning yellow on exposure to light. Nearly insoluble in cold water; soluble in 40 parts of alcohol at 15 °C. (59 °F.), in 250 parts of boiling water, and in 8 parts of boiling alcohol; also soluble in 140 parts of ether, in 4 parts of chloroform, and in solutions of caustic alkalies. When heated to 170 °C. (338 °F.), santonin melts, and forms, if rapidly cooled, an amorphous mass, which instantly crystallizes oil coming in contact with a minute quantity of one of its solvents. At a higher temperature, it sublimes partly unchanged, and, when ignited, it is consumed, leaving no residue. Santonin is neutral to litmus paper moistened with alcohol. Santonin yields, with an alcoholic solution of potassium hydroxide, a bright pinkish-red liquid, which gradually becomes colorless. From its solution in caustic alkalies, santonin is completely precipitated by supersaturation with an acid".[1]
- ^ original source, US Pharmacopoeia, 1898