 | |
 Aqueous solution of Schweizer's reagent
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Tetraamminediaquacopper(II) hydroxide
| |
| Other names
Cuoxam, Schweitzer's reagent
| |
| Identifiers | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.037.720 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| Properties | |
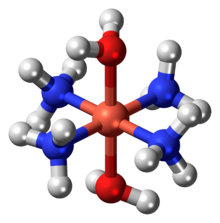
| [Cu(NH3)4(H2O)2](OH)2 | |
| Molar mass | 201.714 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Deep-blue crystalline solid |
| Melting point | decomposes |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Schweizer's reagent is a metal ammine complex with the formula Cu(NH3)4(H2O)2](OH)2. This deep-blue compound is used in purifying cellulose. This salt consists of tetraamminediaquacopper(II) cations ([Cu(NH3)4(H2O)2]2+) and hydroxide anions (OH−).
It is prepared by dissolving copper(II) hydroxide in an aqueous solution of ammonia.
It forms an azure solution. Evaporation of these solutions leaves light blue residue of copper hydroxide, reflecting the lability of the copper-ammonia bonding. If conducted under a stream of ammonia, then deep blue needle-like crystals of the tetrammine form. In presence of oxygen, concentrated solutions give rise to nitrites Cu(NO2)2(NH3)n. The nitrite results from oxidation of the ammonia.[1][2]
- ^ Cudennec, Y.; et al. (1995). "Étude cinétique de l'oxydation de l'ammoniac en présence d'ions cuivriques" [Kinetic study of the oxidation of ammonia in the presence of cupric ions]. Comptes Rendus de l'Académie des Sciences, Série IIB. 320 (6): 309–316.
- ^ Cudennec, Y.; et al. (1993). "Synthesis and study of Cu(NO2)2(NH3)4 and Cu(NO2)2(NH3)2". Eur. J. Solid State Inorg. Chem. 30 (1–2): 77–85.