| Sea of Japan | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
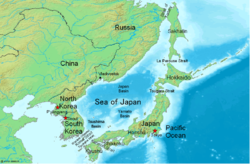 Sea of Japan map | |||||||
| Chinese name | |||||||
| Chinese | 日本海 | ||||||
| |||||||
| Japanese name | |||||||
| Kanji | 日本海 | ||||||
| Hiragana | にほんかい | ||||||
| |||||||
| North Korean name | |||||||
| Chosŏn'gŭl | 조선동해 | ||||||
| Hancha | 朝鮮東海 | ||||||
| Literal meaning | East Sea of Korea | ||||||
| |||||||
| South Korean name | |||||||
| Hangul | 동해 | ||||||
| Hanja | 東海 | ||||||
| Literal meaning | East Sea | ||||||
| |||||||
| Russian name | |||||||
| Russian | Японское море | ||||||
| Romanization | Yaponskoye more | ||||||
| Manchu name | |||||||
| Manchu | ᡩᡝᡵᡤᡳ ᠮᡝᡩᡝᡵᡳ dergi mederi | ||||||
The Sea of Japan is the marginal sea between the Japanese archipelago, Sakhalin, the Korean Peninsula, and the mainland of the Russian Far East. The Japanese archipelago separates the sea from the Pacific Ocean. Like the Mediterranean Sea, it has almost no tides due to its nearly complete enclosure from the Pacific Ocean.[1] This isolation also affects faunal diversity and salinity, both of which are lower than in the open ocean. The sea has no large islands, bays or capes. Its water balance is mostly determined by the inflow and outflow through the straits connecting it to the neighboring seas and the Pacific Ocean. Few rivers discharge into the sea and their total contribution to the water exchange is within 1%.
The seawater has an elevated concentration of dissolved oxygen that results in high biological productivity. Therefore, fishing is the dominant economic activity in the region. The intensity of shipments across the sea has been moderate owing to political issues, but it is steadily increasing as a result of the growth of East Asian economies.
- ^ "Tides in Marginal, Semi-Enclosed and Coastal Seas – Part I: Sea Surface Height". ERC-Stennis at Mississippi State University. Archived from the original on 18 March 2004. Retrieved 2 February 2007.