| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
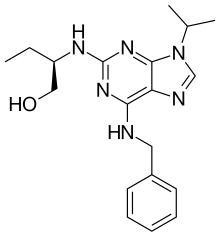
| Preferred IUPAC name
(2R)-2-{[6-(Benzylamino)-9-(propan-2-yl)-9H-purin-2-yl]amino}butan-1-ol | |
| Other names
Roscovitine; CYC202
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| MeSH | roscovitine |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C19H26N6O | |
| Molar mass | 354.458 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Seliciclib (roscovitine or CYC202) is an experimental drug candidate in the family of pharmacological cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK) inhibitors that preferentially inhibit multiple enzyme targets including CDK2, CDK7 and CDK9, which alter the growth phase or state within the cell cycle of treated cells. Seliciclib is being developed by Cyclacel. This is a phase II, dose ranging, multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study.
The aim of this study is to assess the safety of increasing doses of roscovitine administered orally for 4 cycles of 4 consecutive days (treatment "on") separated by a 3 days treatment free period (treatment "off") in adult CF subjects with Cystic Fibrosis carrying 2 Cystic Fibrosis causing mutations with at least one F508del-CFTR mutation and chronically infected with Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
This study involved 36 Cystic Fibrosis patients: 24 treated and 12 controls.[1]
Seliciclib is being researched for the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), Cushing's disease, leukemia, HIV infection, Parkinson's disease, herpes simplex infection, cystic fibrosis[2] and the mechanisms of chronic inflammation disorders.
Seliciclib is a 2,6,9-substituted purine analog. Its structure in complex with CDK2 was determined in 1996.[3] Seliciclib inhibits CDK2/E, CDK2/A, CDK7 and CDK9.[4]
- ^ "A Phase II, Dose Ranging, Multicenter, Double-blind, Placebo Controlled Study to Evaluate Safety and Effects of (R)-Roscovitine in Adults Subjects with Cystic Fibrosis, Carrying 2 Cystic Fibrosis Causing Mutations with at Least One F508del-CFTR Mutation and Chronically Infected with Pseudomonas Aeruginosa, a Study Involving 36 CF Patients (24 Treated, 12 Controls). ROSCO-CF". 11 December 2018.
- ^ Noel S, Faveau C, Norez C, Rogier C, Mettey Y, Becq F (2006). "Discovery of pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyrazines derivatives as submicromolar affinity activators of wild type, G551D, and F508del cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator chloride channels". J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 319 (1): 349–59. doi:10.1124/jpet.106.104521. PMID 16829626. S2CID 1554921.
- ^ De Azevedo WF, Leclerc S, Meijer L, Havlicek L, Strnad M, Kim SH (1997). "Inhibition of cyclin-dependent kinases by purine analogues: crystal structure of human cdk2 complexed with roscovitine". Eur J Biochem. 243 (1–2): 518–526. doi:10.1111/j.1432-1033.1997.0518a.x. PMID 9030780.
- ^ "Cyclacel Begins a Phase IIb Randomized Trial of Seliciclib for Previously Treated Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer". BIOWIRE. June 29, 2006.