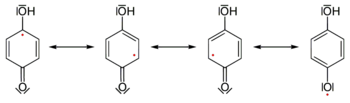
Semiquinones (or ubisemiquinones, if their origin is ubiquinone) are free radicals resulting from the removal of one hydrogen atom with its electron during the process of dehydrogenation of a hydroquinone, such as hydroquinone itself or catechol, to a quinone or alternatively the addition of a single hydrogen atom with its electron to a quinone.[1] Semiquinones are highly unstable.
E.g. ubisemiquinone is the first of two stages in reducing the supplementary form of CoQ10 (ubiquinone) to its active form ubiquinol.
- ^ Song, Y; Buettner, GR (Sep 15, 2010). "Thermodynamic and kinetic considerations for the reaction of semiquinone radicals to form superoxide and hydrogen peroxide". Free Radical Biology & Medicine. 49 (6): 919–62. doi:10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2010.05.009. PMC 2936108. PMID 20493944.