 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Elimination half-life | 4–16 days |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
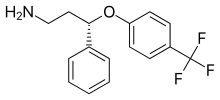
| Formula | C16H16F3NO |
| Molar mass | 295.305 g·mol−1 |
Seproxetine, also known as (S)-norfluoxetine, is a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI).[1][2] It is the S enantiomer of norfluoxetine, the main active metabolite of the widely used antidepressant fluoxetine;[3] it is nearly 4 times more selective for stimulating neurosteroid synthesis relative to serotonin reuptake inhibition than fluoxetine.[4] It is formed through the demethylation, or removal of a methyl group, of fluoxetine.[5] Seproxetine is both an inhibitor of serotonin and dopamine transporters, 5-HT2A and 5-HT2C receptors.[6] It was being investigated by Eli Lilly and Company as an antidepressant; however, it inhibited the KvLQT1 protein, which is responsible for the management of the QT interval. This is the time it takes for the heart to contract and recover. Due to the inhibition, the QT interval was prolonged, which could lead to significant cardiac side complications.[7] Due to this, development of the medication was discontinued.[1] Tests on its efficacy found that it was equivalent to fluoxetine, but sixteen times more powerful than the R enantiomer of norfluoxetine.[8]
- ^ a b "Seproxetine". DrugBank. University of Alberta. Archived from the original on 31 October 2020. Retrieved 10 August 2016.
- ^ de Maat MM, Huitema AD, Mulder JW, Meenhorst PL, van Gorp EC, Mairuhu AT, Beijnen JH (1 October 2003). "Drug Interaction of Fluvoxamine and Fluoxetine with Nevirapine in HIV-1-Infected Individuals". Clinical Drug Investigation. 23 (10): 629–637. doi:10.2165/00044011-200323100-00002. PMID 17535078. S2CID 25958396.
- ^ Anderson IM, Edwards JG (2001). "Guidelines for choice of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor in depressive illness". Advances in Psychiatric Treatment. 7 (3): 170–180. doi:10.1192/apt.7.3.170. ISSN 1355-5146.
- ^ Pinna G, Costa E, Guidotti A (February 2009). "SSRIs act as selective brain steroidogenic stimulants (SBSSs) at low doses that are inactive on 5-HT reuptake". Current Opinion in Pharmacology. 9 (1): 24–30. doi:10.1016/j.coph.2008.12.006. PMC 2670606. PMID 19157982.
- ^ Alvén Fimmerstad T (2022). Could fluorinated pharmaceuticals have an impact on the EOF amount in human blood? (degree of Bachelor thesis). Örebro University.
- ^ Al-Humaidi JY, Refat MS (15 June 2021). "Solution, and solid investigations on the charge–transfer complexation between seproxetine as a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor drug with six kinds of π–electron acceptors". Journal of Molecular Liquids. 332: 115831. doi:10.1016/j.molliq.2021.115831. ISSN 0167-7322. S2CID 233773168.
- ^ "Seproxetine". Inxight Drugs. National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences (NCATS). Archived from the original on 20 April 2023. Retrieved 20 April 2023.
- ^ Wheeler WJ (1992). "An efficient synthesis of S-γ-[(4-trifluoromethyl)-phenoxy]benzenepropanamine-[1-14C] maleate, an important metabolite of fluoxetine hydrochloride". Journal of Labelled Compounds and Radiopharmaceuticals. 31 (2): 119–124. doi:10.1002/jlcr.2580310207.