| |||
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Serine
| |||
| Other names
2-Amino-3-hydroxypropanoic acid
| |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| ChEBI |
| ||
| ChEMBL |
| ||
| ChemSpider | |||
| DrugBank |
| ||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.250 | ||
| EC Number |
| ||
| |||
| KEGG | |||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| UNII |
| ||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties[2] | |||
| C3H7NO3 | |||
| Molar mass | 105.093 g·mol−1 | ||
| Appearance | white crystals or powder | ||
| Density | 1.603 g/cm3 (22 °C) | ||
| Melting point | 246 °C (475 °F; 519 K) decomposes | ||
| soluble | |||
| Acidity (pKa) | 2.21 (carboxyl), 9.15 (amino)[1] | ||
| Supplementary data page | |||
| Serine (data page) | |||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |||
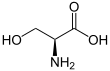
Serine (symbol Ser or S)[3][4] is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an α-amino group (which is in the protonated −NH+
3 form under biological conditions), a carboxyl group (which is in the deprotonated −COO−
form under biological conditions), and a side chain consisting of a hydroxymethyl group, classifying it as a polar amino acid. It can be synthesized in the human body under normal physiological circumstances, making it a nonessential amino acid. It is encoded by the codons UCU, UCC, UCA, UCG, AGU and AGC.
- ^ Dawson, R.M.C., et al., Data for Biochemical Research, Oxford, Clarendon Press, 1959.
- ^ Weast RC, ed. (1981). CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (62nd ed.). Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press. p. C-512. ISBN 0-8493-0462-8.
- ^ "Nomenclature and Symbolism for Amino Acids and Peptides". IUPAC-IUB Joint Commission on Biochemical Nomenclature. 1983. Archived from the original on 9 October 2008. Retrieved 5 March 2018.
- ^ "Nomenclature and symbolism for amino acids and peptides (IUPAC-IUB Recommendations 1983)", Pure Appl. Chem., 56 (5): 595–624, 1984, doi:10.1351/pac198456050595.