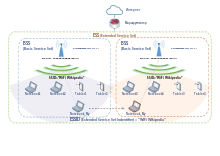
In IEEE 802.11 wireless local area networking standards (including Wi‑Fi), a service set is a group of wireless network devices which share a service set identifier (SSID)—typically the natural language label that users see as a network name. (For example, all of the devices that together form and use a Wi‑Fi network called "Foo" are a service set.) A service set forms a logical network of nodes operating with shared link-layer networking parameters; they form one logical network segment.
A service set is either a basic service set (BSS) or an extended service set (ESS).
A basic service set is a subgroup, within a service set, of devices that share physical-layer medium access characteristics (e.g. radio frequency, modulation scheme, security settings) such that they are wirelessly networked. The basic service set is defined by a basic service set identifier (BSSID) shared by all devices within it. The BSSID is a 48-bit label that conforms to MAC-48 conventions. While a device may have multiple BSSIDs, usually each BSSID is associated with at most one basic service set at a time.[1]
A basic service set should not be confused with the coverage area of an access point, known as the basic service area (BSA).[2]
- ^ "Understanding the Network Terms SSID, BSSID, and ESSID – Technical Documentation – Support – Juniper Networks". www.juniper.net.
- ^ IEEE Std 802.11-2007, § 3.15, p. 5.