This article's lead section may be too short to adequately summarize the key points. (November 2020) |
Single Euro Payments Area | |
|---|---|
 | |
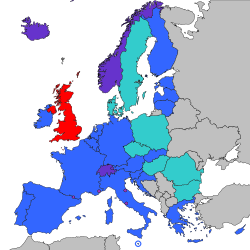 Other members of the European Union Microstates participating in SEPA | |
| Type | Uniform pan-European financial transactions framework |
| Participants | 36 polities
|
| Government | Public-private hybrid administration subject to EU laws |
• Public regulator | Euro Retail Payments Board |
• Private regulator | European Payments Council |
| Currency | Euro (€) |
The Single Euro Payments Area (SEPA) is a payment integration initiative of the European Union for simplification of bank transfers denominated in euros. As of 2020[update], there were 36 members in SEPA,[2] consisting of the 27 member states of the European Union, the four member states of the European Free Trade Association (Iceland, Liechtenstein, Norway and Switzerland), and the United Kingdom.[3][4][2] Some microstates participate in the technical schemes: Andorra,[5] Monaco, San Marino, and Vatican City.[3]
SEPA covers predominantly normal bank transfers. Payment methods which have additional optional features or services, such as mobile phone or smart card payment systems, are not directly covered.[6] However, the instant SEPA payment scheme facilitates payment products also on smart devices.[7]
- ^ "Brexit from 1 January 2021 onwards: get ready for the end of the transition period". European Payments Council. 14 July 2020. Retrieved 31 December 2020.
- ^ a b "SEPA". European Central Bank. 21 January 2020.
- ^ a b "Extension of the geographical scope of SEPA schemes in March 2019". European Payments Council. Archived from the original on 10 August 2022.
- ^ "List of SEPA countries {Updated 2020 version}". B2B Pay powered by Barclays. 7 December 2015.
- ^ "Andorra becomes a member of the Single euro payments area (SEPA) • All PYRENEES · France, Spain, Andorra". 23 June 2018.
- ^ REGULATION (EU) No 260/2012 (article 1 point 3)
- ^ "Instant payments (section "For consumers")". Euro Retail Payments Board (ERPB). 30 May 2023.