| |

| |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Sodium carbonate
| |
| Other names
Soda ash, washing soda, soda crystals, sodium trioxocarbonate
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.007.127 |
| EC Number |
|
| E number | E500(i) (acidity regulators, ...) |
PubChem CID
|
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| Na2CO3 | |
| Molar mass | 105.9888 g/mol (anhydrous) 286.1416 g/mol (decahydrate) |
| Appearance | White solid, hygroscopic |
| Odor | Odorless |
| Density | |
| Melting point | 851 °C (1,564 °F; 1,124 K) (Anhydrous) 100 °C (212 °F; 373 K) decomposes (monohydrate) 33.5 °C (92.3 °F; 306.6 K) decomposes (heptahydrate) 34 °C (93 °F; 307 K) (decahydrate)[2][6] |
Anhydrous, g/100 mL:
| |
| Solubility | Soluble in aq. alkalis,[3] glycerol Slightly soluble in aq. alcohol Insoluble in CS2, acetone, alkyl acetates, alcohol, benzonitrile, liquid ammonia[4] |
| Solubility in glycerine | 98.3 g/100 g (155 °C)[4] |
| Solubility in ethanediol | 3.46 g/100 g (20 °C)[5] |
| Solubility in dimethylformamide | 0.5 g/kg[5] |
| Acidity (pKa) | 10.33 |
| −4.1·10−5 cm3/mol[2] | |
Refractive index (nD)
|
1.485 (anhydrous) 1.420 (monohydrate)[6] 1.405 (decahydrate) |
| Viscosity | 3.4 cP (887 °C)[5] |
| Structure | |
| Monoclinic (γ-form, β-form, δ-form, anhydrous)[7] Orthorhombic (monohydrate, heptahydrate)[1][8] | |
| C2/m, No. 12 (γ-form, anhydrous, 170 K) C2/m, No. 12 (β-form, anhydrous, 628 K) P21/n, No. 14 (δ-form, anhydrous, 110 K)[7] Pca21, No. 29 (monohydrate)[1] Pbca, No. 61 (heptahydrate)[8] | |
| 2/m (γ-form, β-form, δ-form, anhydrous)[7] mm2 (monohydrate)[1] 2/m 2/m 2/m (heptahydrate)[8] | |
a = 8.920(7) Å, b = 5.245(5) Å, c = 6.050(5) Å (γ-form, anhydrous, 295 K)[7] α = 90°, β = 101.35(8)°, γ = 90°
| |
| Octahedral (Na+, anhydrous) | |
| Thermochemistry | |
Heat capacity (C)
|
112.3 J/mol·K[2] |
Std molar
entropy (S⦵298) |
135 J/mol·K[2] |
Std enthalpy of
formation (ΔfH⦵298) |
−1130.7 kJ/mol[2][5] |
Gibbs free energy (ΔfG⦵)
|
−1044.4 kJ/mol[2] |
| Hazards | |
| Occupational safety and health (OHS/OSH): | |
Main hazards
|
Irritant |
| GHS labelling: | |
 [9] [9]
| |
| Warning | |
| H313+H333, H319[9] | |
| P305+P351+P338[9] | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
LD50 (median dose)
|
4090 mg/kg (rat, oral)[10] |
| Safety data sheet (SDS) | MSDS |
| Related compounds | |
Other anions
|
Sodium bicarbonate |
Other cations
|
Lithium carbonate Potassium carbonate Rubidium carbonate Cesium carbonate |
Related compounds
|
Sodium sesquicarbonate Sodium percarbonate |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
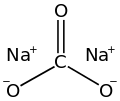
Sodium carbonate (also known as washing soda, soda ash and soda crystals) is the inorganic compound with the formula Na2CO3 and its various hydrates. All forms are white, odourless, water-soluble salts that yield alkaline solutions in water. Historically, it was extracted from the ashes of plants grown in sodium-rich soils, and because the ashes of these sodium-rich plants were noticeably different from ashes of wood (once used to produce potash), sodium carbonate became known as "soda ash".[12] It is produced in large quantities from sodium chloride and limestone by the Solvay process, as well as by carbonating sodium hydroxide which is made using the chloralkali process.
- ^ a b c d Harper, J. P. (1936). Antipov, Evgeny; Bismayer, Ulrich; Huppertz, Hubert; Petrícek, Václav; Pöttgen, Rainer; Schmahl, Wolfgang; Tiekink, E. R. T.; Zou, Xiaodong (eds.). "Crystal Structure of Sodium Carbonate Monohydrate, Na2CO3. H2O". Zeitschrift für Kristallographie - Crystalline Materials. 95 (1): 266–273. doi:10.1524/zkri.1936.95.1.266. ISSN 2196-7105. Retrieved 2014-07-25.
- ^ a b c d e f g Lide, David R., ed. (2009). CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (90th ed.). Boca Raton, Florida: CRC Press. ISBN 978-1-4200-9084-0.
- ^ a b Seidell, Atherton; Linke, William F. (1919). Solubilities of Inorganic and Organic Compounds (2nd ed.). New York: D. Van Nostrand Company. p. 633.
- ^ a b Comey, Arthur Messinger; Hahn, Dorothy A. (February 1921). A Dictionary of Chemical Solubilities: Inorganic (2nd ed.). New York: The MacMillan Company. pp. 208–209.
- ^ a b c d Anatolievich, Kiper Ruslan. "sodium carbonate". chemister.ru. Retrieved 2014-07-25.
- ^ a b Pradyot, Patnaik (2003). Handbook of Inorganic Chemicals. McGraw-Hill. p. 861. ISBN 978-0-07-049439-8.
- ^ a b c d Dusek, Michal; Chapuis, Gervais; Meyer, Mathias; Petricek, Vaclav (2003). "Sodium carbonate revisited" (PDF). Acta Crystallographica Section B. 59 (3): 337–352. Bibcode:2003AcCrB..59..337D. doi:10.1107/S0108768103009017. ISSN 0108-7681. PMID 12761404. Retrieved 2014-07-25.
- ^ a b c Betzel, C.; Saenger, W.; Loewus, D. (1982). "Sodium Carbonate Heptahydrate". Acta Crystallographica Section B. 38 (11): 2802–2804. Bibcode:1982AcCrB..38.2802B. doi:10.1107/S0567740882009996.
- ^ a b c Sigma-Aldrich Co., Sodium carbonate. Retrieved on 2014-05-06.
- ^ Chambers, Michael. "ChemIDplus - 497-19-8 - CDBYLPFSWZWCQE-UHFFFAOYSA-L - Sodium carbonate [NF] - Similar structures search, synonyms, formulas, resource links, and other chemical information".
- ^ "Material Safety Data Sheet – Sodium Carbonate, Anhydrous" (PDF). conservationsupportsystems.com. ConservationSupportSystems. Retrieved 2014-07-25.
- ^ "Soda Ash Statistics and Information". United States Geographical Survey. Retrieved 2024-03-03.
