| |

| |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
| |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider |
|
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
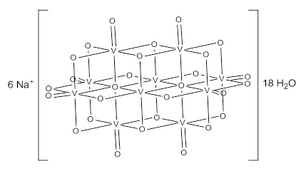
| Na6[V10O28] | |
| Molar mass | 1419.6 g/mol |
| Appearance | orange solid |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Sodium decavanadate describes any member of the family of inorganic compounds with the formula Na6[V10O28](H2O)n. These are sodium salts of the orange-colored decavanadate anion [V10O28]6−.[1] Numerous other decavanadate salts have been isolated and studied since 1956 when it was first characterized.[2]
- ^ Johnson, G.; Murmann, R. K. (1979). "Sodium and Ammonium Decayanadates(V)". Inorganic Syntheses. Vol. 19. pp. 140–145. doi:10.1002/9780470132500.ch32. ISBN 978-0-471-04542-7.
- ^ Rossotti, F. J.; Rossotti, H. (1956). "Equilibrium Studies of Polyanions". Acta Chemica Scandinavica. 10: 957–984. doi:10.3891/acta.chem.scand.10-0957.