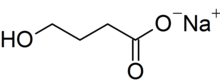 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Xyrem, Lumryz, others[1] |
| Other names | NSC-84223, WY-3478 |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a605032 |
| License data | |
| Addiction liability | High[2][3] |
| Routes of administration | By mouth, intravenous[4] |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 88%[3] |
| Protein binding | <1%[3] |
| Elimination half-life | 0.5 to 1 hour. |
| Excretion | Almost entirely by biotransformation to carbon dioxide, which is then eliminated by expiration |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.007.231 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C4H7NaO3 |
| Molar mass | 126.087 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Sodium oxybate, sold under the brand name Xyrem among others, is a medication used to treat symptoms of narcolepsy: sudden muscle weakness and excessive daytime sleepiness.[3][7][8] It is used sometimes in France and Italy as an anesthetic given intravenously;[9]: 15, 27–28 it is also approved and used in Italy and in Austria to treat alcohol dependence and alcohol withdrawal syndrome.[10]
Sodium oxybate is the sodium salt of γ-hydroxybutyric acid (GHB). The clinical trials for narcolepsy were conducted just as abuse of GHB as a club drug and date rape drug became a matter of public concern. In 2000, GHB was made a Schedule I controlled substance in the United States, while sodium oxybate, when used under an FDA NDA or IND application, was classified as a Schedule III controlled substance for medicinal use under the Controlled Substances Act, with illicit use subject to Schedule I penalties.[11]
Sodium oxybate was approved for use by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) to treat symptoms of narcolepsy in 2002,[3] with a strict risk evaluation and mitigation strategy (REMS) program mandated by the FDA.[3] The US label for sodium oxybate also has a black box warning because it is a central nervous system depressant and may cause respiratory depression, seizures, coma, or death, especially if used in combination with other central nervous system depressants, such as alcohol and its use may cause dependence.[3] In Canada and the European Union it was classified as a Schedule III and a Schedule IV controlled substance, respectively.[12]
It was approved for treating symptoms of narcolepsy in the European Union in 2005.[7]
Orphan Medical had developed it and was acquired by Jazz Pharmaceuticals in 2005. The drug is marketed in Europe by UCB. Jazz Pharmaceuticals raised the price of the drug dramatically after it acquired Orphan,[13] and paid a $20M fine for off-label marketing of the drug in 2007.[14]
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
brandswas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Tay E, Lo WK, Murnion B (2022). "Current Insights on the Impact of Gamma-Hydroxybutyrate (GHB) Abuse". Substance Abuse and Rehabilitation. 13: 13–23. doi:10.2147/SAR.S315720. PMC 8843350. PMID 35173515.
- ^ a b c d e f g h "Xyrem- sodium oxybate solution". DailyMed. Retrieved November 14, 2020.
- ^ Busardò FP, Jones AW (January 2015). "GHB pharmacology and toxicology: acute intoxication, concentrations in blood and urine in forensic cases and treatment of the withdrawal syndrome". Current Neuropharmacology. 13 (1): 47–70. doi:10.2174/1570159X13666141210215423. PMC 4462042. PMID 26074743.
- ^ "FDA-sourced list of all drugs with black box warnings (Use Download Full Results and View Query links.)". nctr-crs.fda.gov. FDA. Retrieved October 22, 2023.
- ^ "Lumryz- sodium oxybate for suspension, extended release". DailyMed. June 7, 2023. Retrieved March 23, 2024.
- ^ a b "UK label Summary of Product Characteristics". Electronic Medicines Compendium. September 8, 2015. Retrieved April 14, 2018.
- ^ "Xyrem (sodium oxybate) Information". Center for Drug Evaluation and Research. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. January 25, 2017.
- ^ "Critical review of gamma-hydroxybutyric acid (GHB)" (PDF). 2012.
- ^ "Alcover: Riassunto delle Caratteristiche del Prodotto". Agenzia Italiana del Farmaco. March 31, 2017. Index page
- ^ "GHB Fact Sheet" (PDF). DEA. Archived from the original (PDF) on April 16, 2018. Retrieved April 16, 2018.
- ^ Wang YG, Swick TJ, Carter LP, Thorpy MJ, Benowitz NL (August 2009). "Safety overview of postmarketing and clinical experience of sodium oxybate (Xyrem): abuse, misuse, dependence, and diversion". Journal of Clinical Sleep Medicine. 5 (4): 365–371. doi:10.5664/jcsm.27549. PMC 2725257. PMID 19968016.
- ^ Staton T (May 7, 2014). "10 big brands keep pumping out big bucks, with a little help from price hikes". Fierce Pharma. Retrieved November 13, 2015.
- ^ "Press release: US Attorney's Office - Eastern District of New York". US Department of Justice. July 13, 2007.