| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
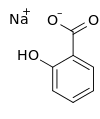
| Preferred IUPAC name
Sodium 2-hydroxybenzoate | |
| Other names
Salsonin, Monosodium salicylate, Sodium o-hydroxybenzoate, Salicylic acid sodium salt, Monosodium 2-hydroxybenzoate, Diuratin
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| DrugBank | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.181 |
| EC Number |
|
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C7H5NaO3 | |
| Molar mass | 160.104 g/mol |
| Appearance | White crystals |
| Melting point | 200 °C (392 °F; 473 K) |
| 25.08 g/100 g (-1.5 °C) 107.9 g/100 g (15 °C) 124.6 g/100 g (25 °C) 141.8 g/100 g (78.5 °C) 179 g/100 g (114 °C)[1] | |
| Solubility | Soluble in glycerol, 1,4-Dioxane, alcohol[1] |
| Solubility in methanol | 26.28 g/100 g (15 °C) 34.73 g/100 g (67.2 °C)[1] |
| Pharmacology | |
| N02BA04 (WHO) | |
| Hazards | |
| Occupational safety and health (OHS/OSH): | |
Main hazards
|
Harmful |
Eye hazards
|
Irritant |
| GHS labelling:[3] | |

| |
| Warning | |
| H314, H331, H400 | |
| P210, P261, P273, P280, P305+P351+P338, P310 | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| 250 °C (482 °F; 523 K) | |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
LD50 (median dose)
|
930 mg/kg (rats, oral)[2] |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Sodium salicylate is a sodium salt of salicylic acid. It can be prepared from sodium phenolate and carbon dioxide under higher temperature and pressure. Historically, it has been synthesized by refluxing methyl salicylate (wintergreen oil) with an excess of sodium hydroxide.[4]
- ^ a b c "sodium salicylate". chemister.ru. Retrieved 8 April 2018.
- ^ Chambers, Michael. "ChemIDplus - 54-21-7 - ABBQHOQBGMUPJH-UHFFFAOYSA-M - Sodium salicylate [USP:JAN] - Similar structures search, synonyms, formulas, resource links, and other chemical information". chem.sis.nlm.nih.gov. Retrieved 8 April 2018.
- ^ Sigma-Aldrich Co., Sodium salicylate. Retrieved on 2014-05-26.
- ^ Lehman, J.W., Operational Organich Chemistry, 4th ed., New Jersey, Prentice Hall, 2009
