| Granulometry | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Basic concepts | |
| Particle size, Grain size, Size distribution, Morphology | |
| Methods and techniques | |
| Mesh scale, Optical granulometry, Sieve analysis, Soil gradation | |
Related concepts | |
| Granulation, Granular material, Mineral dust, Pattern recognition, Dynamic light scattering | |
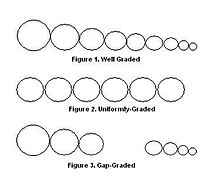
In soil science, soil gradation is a classification of a coarse-grained soil that ranks the soil based on the different particle sizes contained in the soil.[1] Soil gradation is an important aspect of soil mechanics and geotechnical engineering because it is an indicator of other engineering properties such as compressibility, shear strength, and hydraulic conductivity. In a design, the gradation of the in situ (on site) soil often controls the design and ground water drainage of the site. A poorly graded soil will have better drainage than a well graded soil,[2] if it is not high in clay quality.
Soil is graded as either well graded or poorly graded.[3] Soil gradation is determined by analyzing the results of a sieve analysis [4] [5] or a hydrometer analysis.[1]
The process for grading a soil is in accordance with either the Unified Soil Classification System or the AASHTO Soil Classification System. Gradation of a soil is determined by reading the grain size distribution curve produced from the results of laboratory tests on the soil. Gradation of a soil can also be determined by calculating the coefficient of uniformity, Cu, and the coefficient of curvature, Cc, of the soil and comparing the calculated values with published gradation limits.[1][6]
- ^ a b c Holtz, R. and Kovacs, W. (1981), An Introduction to Geotechnical Engineering, Prentice-Hall, Inc. ISBN 0-13-484394-0
- ^ "ASTM D6913 - 04(2009)".ASTM International. ASTM International. 1996-2009. October 13, 2009.
- ^ “Soil Gradation”. Integrated Publishing. Integrated Publishing. 2003-2007. October 13, 2009.
- ^ “Sieve Analysis and Particle Analysis Archived 2009-12-28 at the Wayback Machine”. Grand Solution Manual. SJ Soft Technologies. 2008. October 13, 2009.
- ^ “Sieve Analysis”. Integrated Publishing. Integrated Publishing. 2003-2007. October 13, 2009.
- ^ Coduto, Donald P. Foundation Design Principles and Practices (2nd Edition). 02nd ed. Upper Saddle River: Prentice Hall, 2000. Print. ISBN 0-13-589706-8