
| Part of a series of articles on |
| Nanomaterials |
|---|
 |
| Carbon nanotubes |
| Fullerenes |
| Other nanoparticles |
| Nanostructured materials |
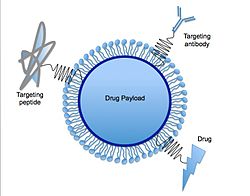
Lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) are very small spherical particles composed of lipids. They are a novel pharmaceutical drug delivery system (part of nanoparticle drug delivery), and a novel pharmaceutical formulation.[1][2] Using LNPs for drug delivery was first approved in 2018 for the siRNA drug Onpattro.[3] LNPs became more widely known in late 2020, as some COVID-19 vaccines that use RNA vaccine technology coat the fragile mRNA strands with PEGylated lipid nanoparticles as their delivery vehicle (including both the Moderna and the Pfizer–BioNTech COVID-19 vaccines).[4]
- ^ Saupe, Anne; Rades, Thomas (2006). "Solid Lipid Nanoparticles". Nanocarrier Technologies. pp. 41–50. doi:10.1007/978-1-4020-5041-1_3. ISBN 978-1-4020-5040-4.
- ^ Jenning, V; Thünemann, AF; Gohla, SH (2000). "Characterisation of a novel solid lipid nanoparticle carrier system based on binary mixtures of liquid and solid lipids". International Journal of Pharmaceutics. 199 (2): 167–77. doi:10.1016/S0378-5173(00)00378-1. PMID 10802410.
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
Stat4was invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Pardi, Norbert; Hogan, Michael J.; Porter, Frederick W.; Weissman, Drew (April 2018). "mRNA vaccines — a new era in vaccinology". Nature Reviews Drug Discovery. 17 (4): 261–279. doi:10.1038/nrd.2017.243. PMC 5906799. PMID 29326426.