| South Fork Eel River | |
|---|---|
 Meander in the South Fork Eel River | |
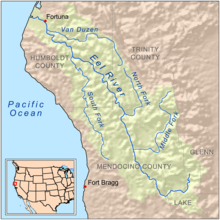 Map of the Eel River drainage basin showing the South Fork | |
| Location | |
| Country | United States |
| State | California |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Source | |
| • location | Branscomb, California |
| • coordinates | 39°36′46″N 123°29′34″W / 39.61278°N 123.49278°W[1] |
| • elevation | 2,500 ft (760 m) |
| Mouth | Eel River |
• location | Dyerville/Founders' Grove, California |
• coordinates | 40°21′21″N 123°55′10″W / 40.35583°N 123.91944°W[1] |
• elevation | 100 ft (30 m) |
| Length | 105 mi (169 km) |
| Basin size | 689 sq mi (1,780 km2) |
| Discharge | |
| • location | USGS gage 11476500, near Miranda, CA, river mile 20[2] |
| • average | 1,845 cu ft/s (52.2 m3/s)[2] |
| • minimum | 10 cu ft/s (0.28 m3/s) |
| • maximum | 199,000 cu ft/s (5,600 m3/s) |
| Basin features | |
| Tributaries | |
| • left | Hollow Tree Creek, Bull Creek (California) |
| • right | Tenmile Creek (South Fork Eel River), Rattlesnake Creek (California), Cedar Creek (South Fork Eel River), East Branch South Fork Eel River |
| Designated | January 19, 1981 |
The South Fork Eel River is the largest tributary of the Eel River in north-central California in the United States. The river flows 105 miles (169 km) north from Laytonville to Dyerville/Founders' Grove where it joins the Eel River. The South Fork drains a long and narrow portion of the Coast Range of California in parts of Mendocino and Humboldt counties. U.S. Route 101 follows the river for much of its length.[3]
The Kai Pomo, a branch of the Pomo people, once lived in the upper portion of the watershed.[4] Before industrial development in the 1800s, many native tribes relied on the river's abundant runs of salmon and steelhead. In the 1920s, a private company built the Benbow Dam, blocking fish migration to a large area of the basin.[5]
The South Fork is designated as a National Wild and Scenic River from the confluence of Section Four Creek to the mouth.
- ^ a b U.S. Geological Survey Geographic Names Information System: South Fork Eel River, United States Geological Survey, GNIS
- ^ a b Cite error: The named reference
wdrwas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ "South Fork Eel River Basin". California Coastal Watershed Program. coastalwatersheds.ca.gov. Archived from the original on 2009-07-03. Retrieved 2009-07-04.
- ^ Barrett, p. 279
- ^ "Big Problem, Little Dam". North Coast Journal. www.northcoastjournal.com. 5 July 2001. Retrieved 2009-07-04.