This article needs additional citations for verification. (January 2009) |
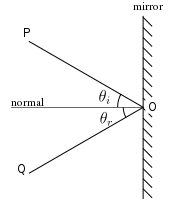

Specular reflection, or regular reflection, is the mirror-like reflection of waves, such as light, from a surface.[1]
The law of reflection states that a reflected ray of light emerges from the reflecting surface at the same angle to the surface normal as the incident ray, but on the opposing side of the surface normal in the plane formed by the incident and reflected rays. This behavior was first described by Hero of Alexandria (AD c. 10–70).[2] Later, Alhazen gave a complete statement of the law of reflection.[3][4][5] He was first to state that the incident ray, the reflected ray, and the normal to the surface all lie in a same plane perpendicular to reflecting plane.[6][7]
Specular reflection may be contrasted with diffuse reflection, in which light is scattered away from the surface in a range of directions.
- ^ Tan, R.T. (2013), Ikeuchi, Katsushi (ed.), Specularity, Specular Reflectance. In: Ikeuchi K. (eds) Computer Vision (PDF), Springer, Boston, MA, doi:10.1007/978-0-387-31439-6, ISBN 978-0-387-31439-6, S2CID 5058976
- ^ Sir Thomas Little Heath (1981). A history of Greek mathematics. Volume II: From Aristarchus to Diophantus. ISBN 978-0-486-24074-9.
- ^ Stamnes, J. J. (2017-11-13). Waves in Focal Regions: Propagation, Diffraction and Focusing of Light, Sound and Water Waves. Routledge. ISBN 978-1-351-40468-6.
- ^ Mach, Ernst (2013-01-23). The Principles of Physical Optics: An Historical and Philosophical Treatment. Courier Corporation. ISBN 978-0-486-17347-4.
- ^ Iizuka, Keigo (2013-11-11). Engineering Optics. Springer Science & Business Media. ISBN 978-3-662-07032-1.
- ^ Selin 2008, p. 1817.
- ^ Mach, Ernst (2013-01-23). The Principles of Physical Optics: An Historical and Philosophical Treatment. Courier Corporation. ISBN 978-0-486-17347-4.
