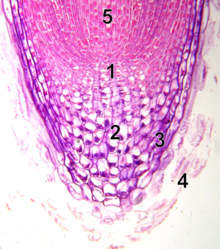

Statocytes are gravity-sensing (gravitropic) cells in higher plants.[1] They contain amyloplasts-statoliths – starch-filled amyloplastic organelles – which sediment at the lowest part of the cells. In the roots, sedimentation of the statoliths towards the lower part of the statocytes constitutes a signal for the production and redistribution of auxin. When stems or roots are not exactly aligned with the gravity vector, statoliths move and adjust to gravity. This is followed by a triggering of the asymmetrical distribution of auxin that causes the curvature and growth of stems against the gravity vector, as well as growth of roots along the gravity vector. Statocytes are present in the elongating region of coleoptiles, shoots and inflorescence stems. In roots, the root cap is the only place where sedimentation is observed, and only the central columella cells of the root cap serve as gravity-sensing statocytes.[2] They can initiate differential growth patterns, bending the root towards the vertical axis.[3]
With optical microscopy and the right fixation technique, it is possible to observe the cells in the root tip, where statocytes containing statoliths are situated in the root cap. The statoliths have sunk to the lowest part of the cell where they make contact with the plasma membrane. It is this contact that might be responsible for triggering the release or redistribution of auxin, although the exact molecular mechanisms by which the accumulation of statoliths at the bottom of the cell regulates the distribution of auxin are not yet fully understood.[4] A uniform concentration of auxin causes the root to grow straight down. This is a form of positive gravitropism where the root grows along the gravity vector. Should the root lie horizontally, then the statoliths will displace sideways to the cell membrane and induce a change in auxin distribution that triggers the root to bend and grow straight down.[5]
- ^ D. Volkmann & M. Tewinkel for the European Space Agency (April 1997). "Position of Statoliths in Statocytes from Cress Roots under Changing Gravity Conditions". European Space Agency. Retrieved 2008-12-12.
- ^ van Loon, Jack J. W. A. (22 August 2007). "The Gravity Environment in Space Experiments". Biology in Space and Life on Earth (1 ed.). Wiley. pp. 17–32. ISBN 978-3-527-40668-5.
- ^ Neela Shiva Kumar, Martin Henry H. Stevens and John Z. Kiss (2008-02-01). "Plastid movement in statocytes of the arg1 (altered response to gravity) mutant". American Journal of Botany. Archived from the original on July 6, 2008. Retrieved 2008-12-14.
- ^ Nishimura, Takeshi; Mori, Shogo; Shikata, Hiromasa; Nakamura, Moritaka; Hashiguchi, Yasuko; Abe, Yoshinori; Hagihara, Takuma; Yoshikawa, Hiroshi Y.; Toyota, Masatsugu; Higaki, Takumi; Morita, Miyo Terao (2023-08-10). "Cell polarity linked to gravity sensing is generated by LZY translocation from statoliths to the plasma membrane". Science. doi:10.1126/science.adh9978. ISSN 0036-8075.
- ^ Volkmann, D.; Buchen, B.; Hejnowicz, Z.; Tewinkel, M.; Sievers, A. (1991). "Oriented movement of statoliths studied in a reduced gravitational field during parabolic flights of rockets". Planta. 185: 153–161. ISSN 0032-0935. PMID 11538120.