| |||
| |||
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Styrene[2]
| |||
| Systematic IUPAC name
Ethenylbenzene[1] | |||
| Other names | |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| 1071236 | |||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChEMBL | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.002.592 | ||
| EC Number |
| ||
| 2991 | |||
| KEGG | |||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| RTECS number |
| ||
| UNII | |||
| UN number | 2055 | ||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C8H8 | |||
| Molar mass | 104.15 g/mol | ||
| Appearance | colorless oily liquid | ||
| Odor | sweet, floral[3] | ||
| Density | 0.909 g/cm3 | ||
| Melting point | −30 °C (−22 °F; 243 K) | ||
| Boiling point | 145 °C (293 °F; 418 K) | ||
| 0.03% (20 °C)[3] | |||
| log P | 2.70[4] | ||
| Vapor pressure | 5 mmHg (20 °C)[3] | ||
| −6.82×10−5 cm3/mol | |||
Refractive index (nD)
|
1.5469 | ||
| Viscosity | 0.762 cP at 20 °C | ||
| Structure | |||
| 0.13 D | |||
| Hazards | |||
| Occupational safety and health (OHS/OSH): | |||
Main hazards
|
flammable, toxic, probably carcinogenic | ||
| GHS labelling: | |||
  
| |||
| Danger | |||
| H226, H315, H319, H332, H361, H372 | |||
| P201, P202, P210, P233, P240, P241, P242, P243, P260, P261, P264, P270, P271, P280, P281, P302+P352, P303+P361+P353, P304+P312, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P308+P313, P312, P314, P321, P332+P313, P337+P313, P362, P370+P378, P403+P235, P405, P501 | |||
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |||
| Flash point | 31 °C (88 °F; 304 K) | ||
| Explosive limits | 0.9–6.8%[3] | ||
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |||
LC50 (median concentration)
|
2194 ppm (mouse, 4 h) 5543 ppm (rat, 4 h)[5] | ||
LCLo (lowest published)
|
10,000 ppm (human, 30 min) 2771 ppm (rat, 4 h)[5] | ||
| NIOSH (US health exposure limits): | |||
PEL (Permissible)
|
TWA 100 ppm C 200 ppm 600 ppm (5-minute maximum peak in any 3 hours)[3] | ||
REL (Recommended)
|
TWA 50 ppm (215 mg/m3) ST 100 ppm (425 mg/m3)[3] | ||
IDLH (Immediate danger)
|
700 ppm[3] | ||
| Safety data sheet (SDS) | MSDS | ||
| Related compounds | |||
Related styrenes;
related aromatic compounds |
polystyrene, stilbene; ethylbenzene | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |||
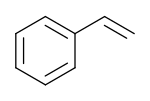
Styrene is an organic compound with the chemical formula C6H5CH=CH2. Its structure consists of a vinyl group as substituent on benzene. Styrene is a colorless, oily liquid, although aged samples can appear yellowish. The compound evaporates easily and has a sweet smell, although high concentrations have a less pleasant odor.[vague] Styrene is the precursor to polystyrene and several copolymers, and is typically made from benzene for this purpose. Approximately 25 million tonnes of styrene were produced in 2010,[6] increasing to around 35 million tonnes by 2018.
- ^ a b "Front Matter". Nomenclature of Organic Chemistry: IUPAC Recommendations and Preferred Names 2013 (Blue Book). Cambridge: Royal Society of Chemistry. 2014. pp. P001–P004. doi:10.1039/9781849733069-FP001. ISBN 978-0-85404-182-4.
- ^ pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/7501#section=IUPAC-Name&fullscreen=true
- ^ a b c d e f g NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards. "#0571". National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- ^ "Styrene". www.chemsrc.com.
- ^ a b "Styrene". Immediately Dangerous to Life or Health Concentrations (IDLH). National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- ^ "New Process for Producing Styrene Cuts Costs, Saves Energy, and Reduces Greenhouse Gas Emissions" (PDF). US Department of Energy. Archived from the original (PDF) on 21 April 2013.