This article needs additional citations for verification. (January 2020) |
| Subclavian artery | |
|---|---|
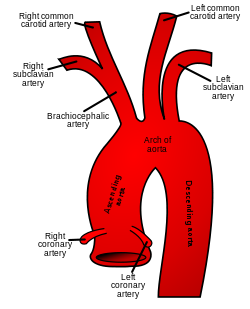 Schematic of the proximal aorta and its branches. The left subclavian artery is the fifth branch of the aorta and the third branch from the arch of the aorta. The right subclavian artery arises from the brachiocephalic artery and its branches. (Right subclavian is at upper left, and left subclavian is at upper right.) | |
| Details | |
| Source | Aortic arch (left) Brachiocephalic (right) |
| Branches | Vertebral artery internal thoracic artery thyrocervical trunk costocervical trunk dorsal scapular artery (mostly) |
| Vein | Subclavian vein |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | arteria subclavia |
| MeSH | D013348 |
| TA98 | A12.2.08.001 |
| TA2 | 4537 |
| FMA | 3951 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
In human anatomy, the subclavian arteries are paired major arteries of the upper thorax, below the clavicle. They receive blood from the aortic arch. The left subclavian artery supplies blood to the left arm and the right subclavian artery supplies blood to the right arm, with some branches supplying the head and thorax. On the left side of the body, the subclavian comes directly off the aortic arch, while on the right side it arises from the relatively short brachiocephalic artery when it bifurcates into the subclavian and the right common carotid artery.
The usual branches of the subclavian on both sides of the body are the vertebral artery, the internal thoracic artery, the thyrocervical trunk, the costocervical trunk and the dorsal scapular artery, which may branch off the transverse cervical artery, which is a branch of the thyrocervical trunk. The subclavian becomes the axillary artery at the lateral border of the first rib.