| |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
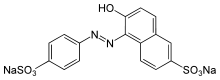
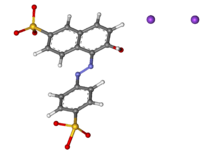
Disodium 6-hydroxy-5-[(4-sulfophenyl)azo]-2-naphthalenesulfonate
| |
Other names
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.018.629 |
| E number | E110 (colours) |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C16H10N2Na2O7S2 | |
| Molar mass | 452.36 g·mol−1 |
| Melting point | 300 °C (572 °F; 573 K) |
| Hazards | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Sunset yellow FCF (also known as orange yellow S, or C.I. 15985) is a petroleum-derived orange azo dye with a pH-dependent maximum absorption at about 480 nm at pH 1 and 443 nm at pH 13, with a shoulder at 500 nm.[1][2]: 463 When added to foods sold in the United States, it is known as FD&C Yellow 6; when sold in Europe, it is denoted by E Number E110.[3]
- ^ Cite error: The named reference
EncycFoodSafetywas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ Committee on Food Chemicals Codex (2003). Food chemicals codex (5th ed.). Washington, DC: National Academy Press. ISBN 9780309088664.
- ^ Wood, Roger M. (2004). Analytical methods for food additives. Boca Raton: CRC Press. ISBN 1-85573-722-1.
